While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Earth & Climate
Uncovering Hidden Risks: A Study on the Türkiye Gold Mine Landslide Highlights Need for Future Monitoring
A new analysis of a fatal landslide that occurred on 13 February 2024 at the pler Gold Mine in Turkiye reveals that the site of the landslide had been slowly moving for at least four years prior to the failure.

Air Quality
Greenland’s Glacial Runoff Fuels Explosive Growth in Ocean Life
NASA-backed simulations reveal that meltwater from Greenland’s Jakobshavn Glacier lifts deep-ocean nutrients to the surface, sparking large summer blooms of phytoplankton that feed the Arctic food web.
Atmosphere
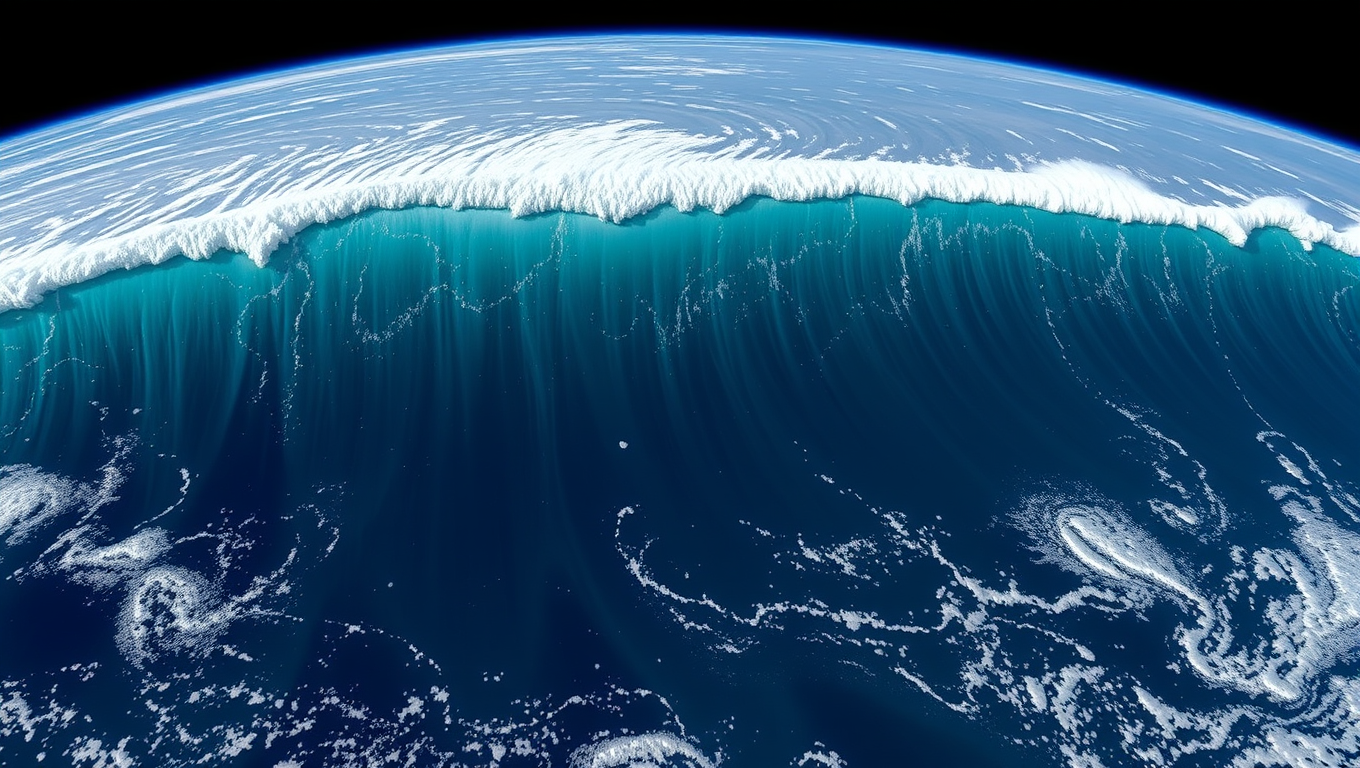
NASA’s SWOT Satellite Captures Kamchatka Megaquake Tsunami in Stunning Detail
When a massive 8.8 magnitude earthquake struck off Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula, NASA and CNES’s SWOT satellite captured a rare and detailed picture of the tsunami that followed. Recorded just over an hour after the quake, the satellite revealed the wave’s height, shape, and path, offering scientists an unprecedented multidimensional view from space.
Climate
The Ocean’s Fragile Fortresses: Uncovering the Impact of Climate Change on Bryozoans
Mediterranean bryozoans, including the “false coral,” are showing alarming changes in structure and microbiomes under acidification and warming. Field studies at volcanic CO₂ vents reveal that these stressors combined sharply reduce survival, posing risks to marine ecosystems.
-

 Detectors9 months ago
Detectors9 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate10 months ago
Earth & Climate10 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer10 months ago
Cancer10 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein10 months ago
Albert Einstein10 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry10 months ago
Chemistry10 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate10 months ago
Earth & Climate10 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Agriculture and Food10 months ago
Agriculture and Food10 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions10 months ago
Diseases and Conditions10 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention