While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Communications
Hexagons for Data Protection: A New Method for Location Proofing without Personal Data Disclosure
Location data is considered particularly sensitive — its misuse can have serious consequences. Researchers have now developed a method that allows individuals to cryptographically prove their location — without revealing it. The foundation of this method is the so-called zero-knowledge proof with standardized floating-point numbers.

Artificial Intelligence
Accelerating Evolution: The Power of T7-ORACLE in Protein Engineering
Researchers at Scripps have created T7-ORACLE, a powerful new tool that speeds up evolution, allowing scientists to design and improve proteins thousands of times faster than nature. Using engineered bacteria and a modified viral replication system, this method can create new protein versions in days instead of months. In tests, it quickly produced enzymes that could survive extreme doses of antibiotics, showing how it could help develop better medicines, cancer treatments, and other breakthroughs far more quickly than ever before.
Artificial Intelligence
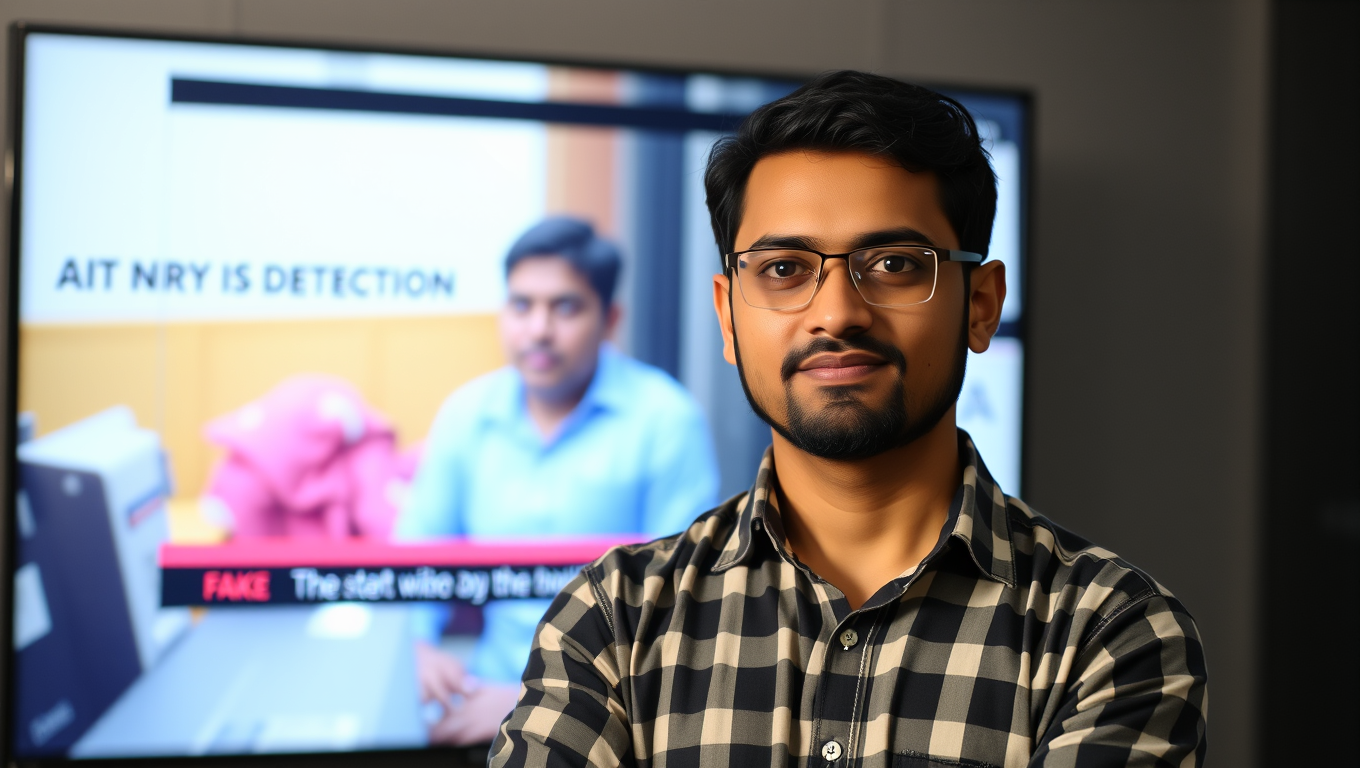
Google’s Deepfake Hunter: Exposing Manipulated Videos with a Universal Detector
AI-generated videos are becoming dangerously convincing and UC Riverside researchers have teamed up with Google to fight back. Their new system, UNITE, can detect deepfakes even when faces aren’t visible, going beyond traditional methods by scanning backgrounds, motion, and subtle cues. As fake content becomes easier to generate and harder to detect, this universal tool might become essential for newsrooms and social media platforms trying to safeguard the truth.
Artificial Intelligence
The Quantum Drumhead Revolution: A Breakthrough in Signal Transmission with Near-Perfect Efficiency
Researchers have developed an ultra-thin drumhead-like membrane that lets sound signals, or phonons, travel through it with astonishingly low loss, better than even electronic circuits. These near-lossless vibrations open the door to new ways of transferring information in systems like quantum computers or ultra-sensitive biological sensors.
-

 Detectors11 months ago
Detectors11 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate12 months ago
Earth & Climate12 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer12 months ago
Cancer12 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein12 months ago
Albert Einstein12 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry12 months ago
Chemistry12 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate12 months ago
Earth & Climate12 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Diseases and Conditions12 months ago
Diseases and Conditions12 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention
-

 Agriculture and Food12 months ago
Agriculture and Food12 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”