While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Child Development
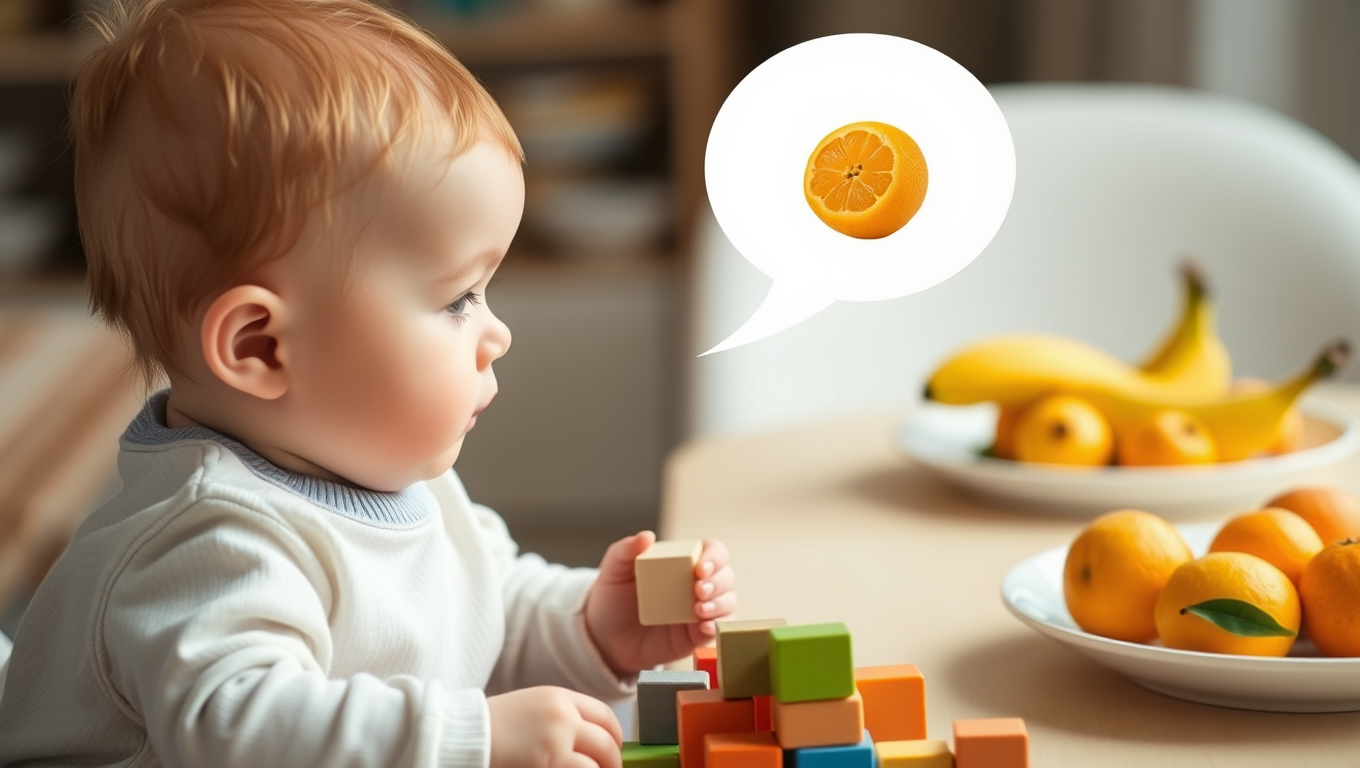
Little Minds Big Learning: 15-Month-Old Infants Learn New Words for Objects from Conversations Alone
A new study by developmental scientists offers the first evidence that infants as young as 15 months can identify an object they have learned about from listening to language — even if the object remains hidden.

Autism
The Thalamic Feedback Loop: Unveiling the Brain’s Secret Pathway to Sensory Perception
Sometimes a gentle touch feels sharp and distinct, other times it fades into the background. This inconsistency isn’t just mood—it’s biology. Scientists found that the thalamus doesn’t just relay sensory signals—it fine-tunes how the brain responds to them, effectively changing what we feel. A hidden receptor in the cortex seems to prime neurons, making them more sensitive to touch.
Child Development
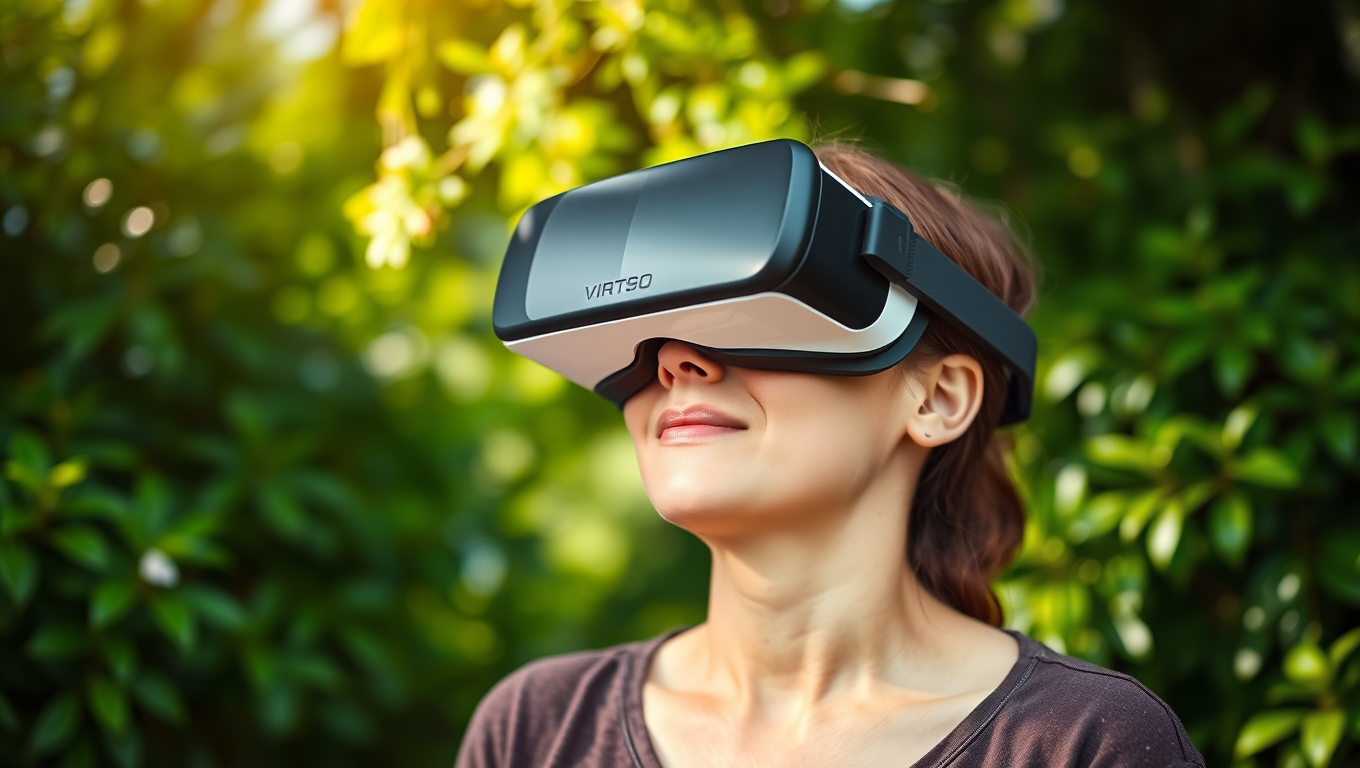
Pain Relief Without Pills? VR Nature Scenes Activate Brain’s Healing Switch
Stepping into a virtual forest or waterfall scene through VR could be the future of pain management. A new study shows that immersive virtual nature dramatically reduces pain sensitivity almost as effectively as medication. Researchers at the University of Exeter found that the more present participants felt in these 360-degree nature experiences, the stronger the pain-relieving effects. Brain scans confirmed that immersive VR scenes activated pain-modulating pathways, revealing that our brains can be coaxed into suppressing pain by simply feeling like we re in nature.
Alternative Medicine
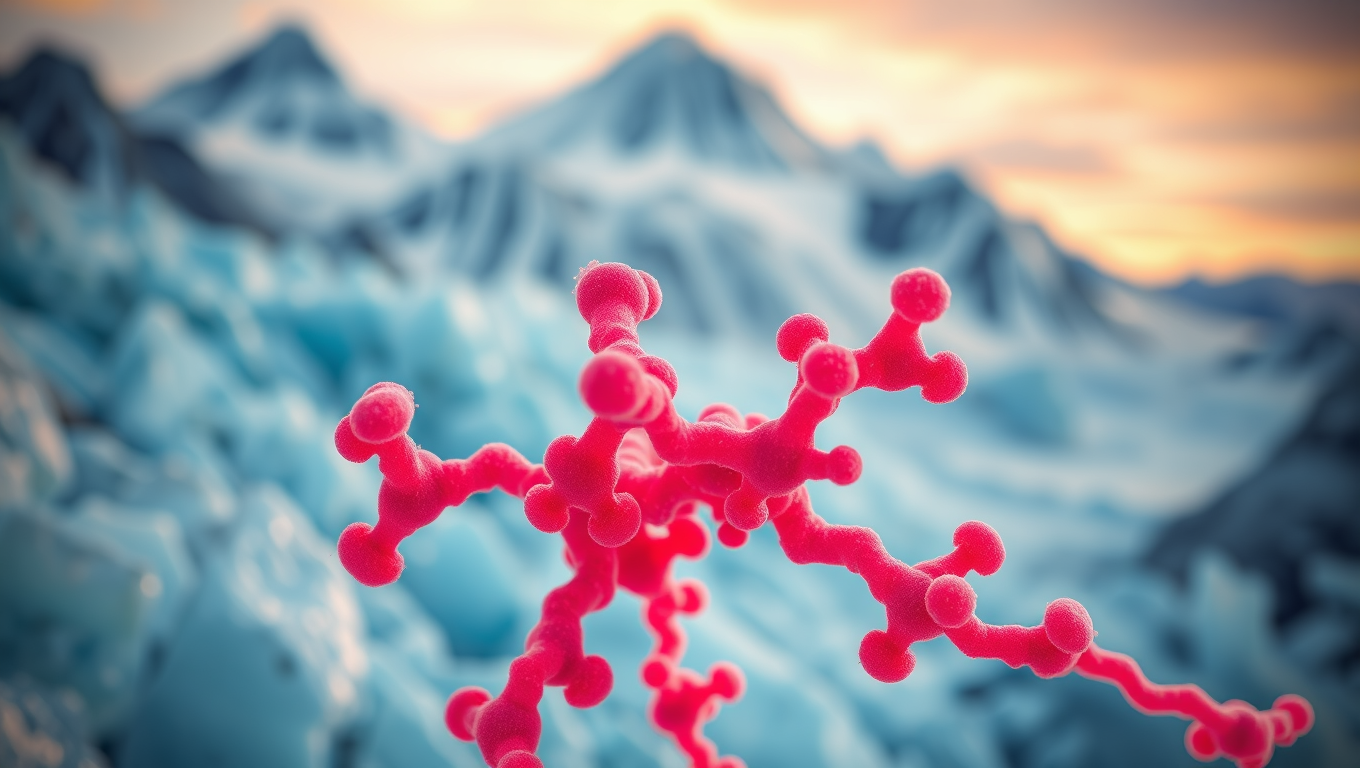
Unlocking the Secrets of Cryorhodopsins: How Arctic Microbes Could Revolutionize Neuroscience
In the frozen reaches of the planet—glaciers, mountaintops, and icy groundwater—scientists have uncovered strange light-sensitive molecules in tiny microbes. These “cryorhodopsins” can respond to light in ways that might let researchers turn brain cells on and off like switches. Some even glow blue, a rare and useful trait for medical applications. These molecules may help the microbes sense dangerous UV light in extreme environments, and scientists believe they could one day power new brain tech, like light-based hearing aids or next-level neuroscience tools—all thanks to proteins that thrive in the cold and shimmer under light.
-

 Detectors10 months ago
Detectors10 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer11 months ago
Cancer11 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein11 months ago
Albert Einstein11 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry10 months ago
Chemistry10 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Agriculture and Food11 months ago
Agriculture and Food11 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions11 months ago
Diseases and Conditions11 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention