Sometimes a gentle touch feels sharp and distinct, other times it fades into the background. This inconsistency isn’t just mood—it’s biology. Scientists found that the thalamus...



A groundbreaking study from Flinders University reveals that it's not just making eye contact that matters, but precisely when and how you do it. By studying...


Researchers are using an advanced brain imaging method called MEG to understand why Parkinson’s drug levodopa doesn’t work equally well for everyone. By mapping patients’ brain...
Deleting a gene called PTEN in certain brain cells disrupts the brain’s fear circuitry and triggers anxiety-like behavior in mice — key traits seen in autism....
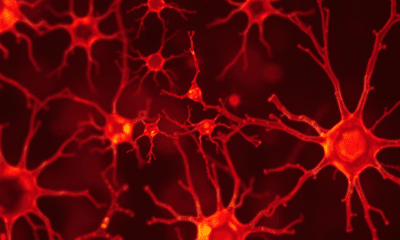
A team at Kobe University has created a game-changing resource for autism research: 63 mouse embryonic stem cell lines, each carrying a genetic mutation strongly associated...
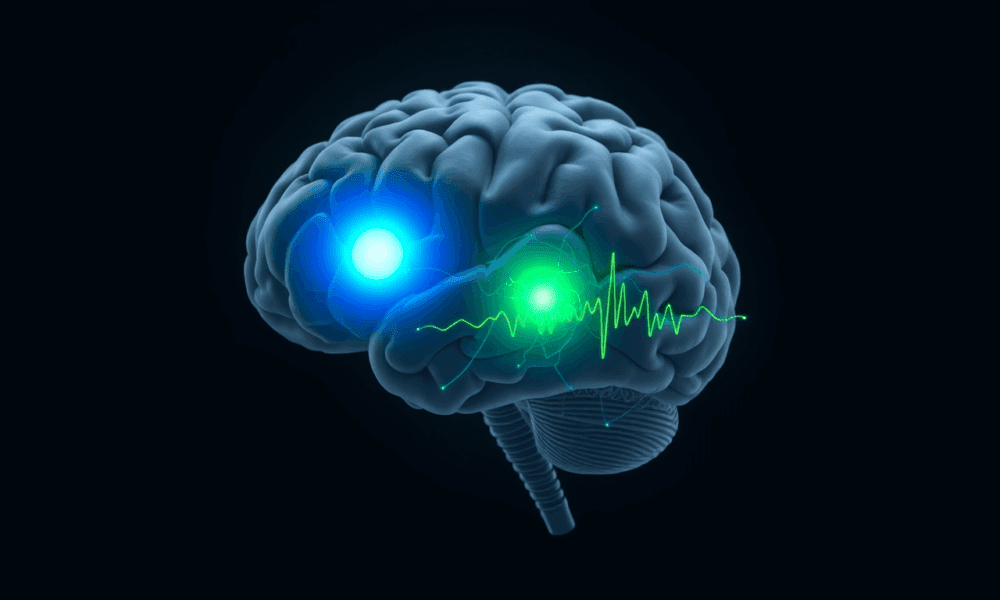

A new study challenges a decades-old assumption in neuroscience by showing that the brain uses distinct transmission sites -- not a shared site -- to achieve...


How come you can't tickle yourself? And why can some people handle tickling perfectly fine while others scream their heads off? Neuroscientists argue that we should...
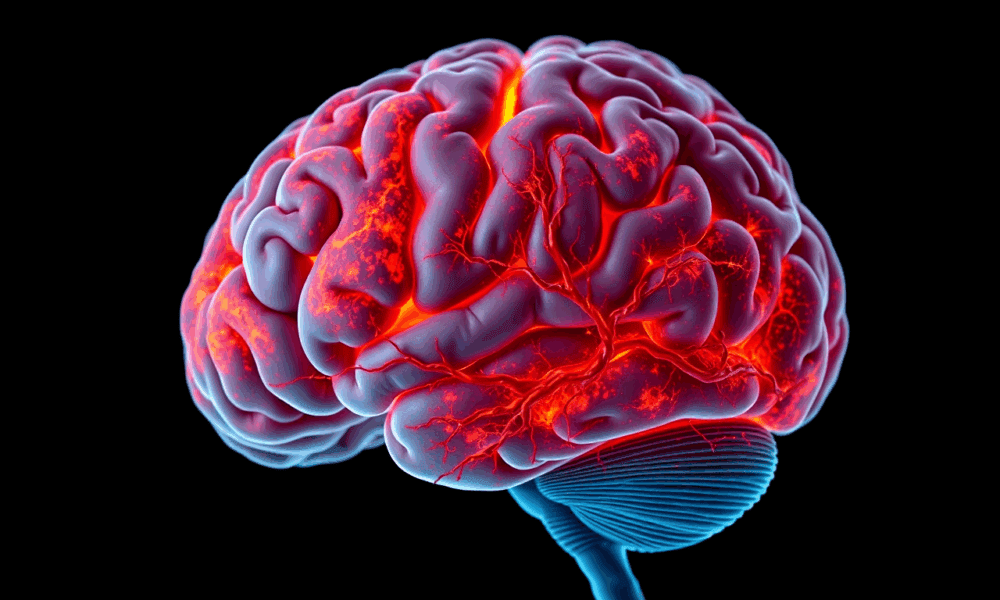
A study reveals that inflammation associated with Marfan syndrome increases vulnerability to neurological diseases and complications following strokes, as demonstrated in animal models.



There is no significant difference in the effectiveness of how autistic and non-autistic people communicate, according to a new study, challenging the stereotype that autistic people...


Researchers have identified the neural mechanisms in the brain that regulate both positive and negative impressions of a social encounter, as well as how an imbalance...