

What made ribose the sugar of choice for life's code? Scientists at Scripps Research may have cracked a major part of this mystery. Their experiments show...
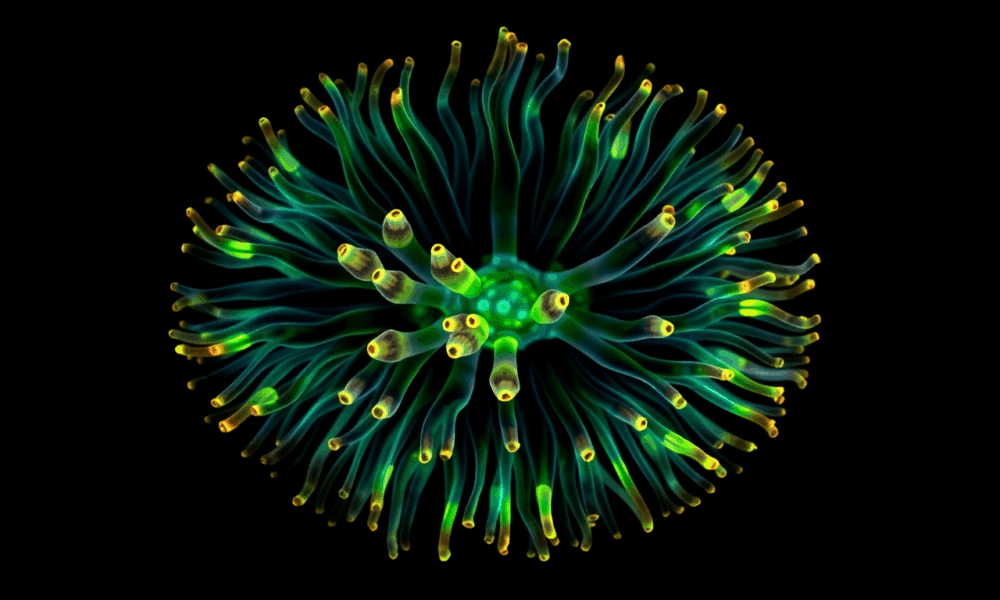
Sea anemones may hold the key to the ancient origins of body symmetry. A study from the University of Vienna shows they use a molecular mechanism...


Scientists found out how naturally unstable filaments decide whether to grow or to shorten.
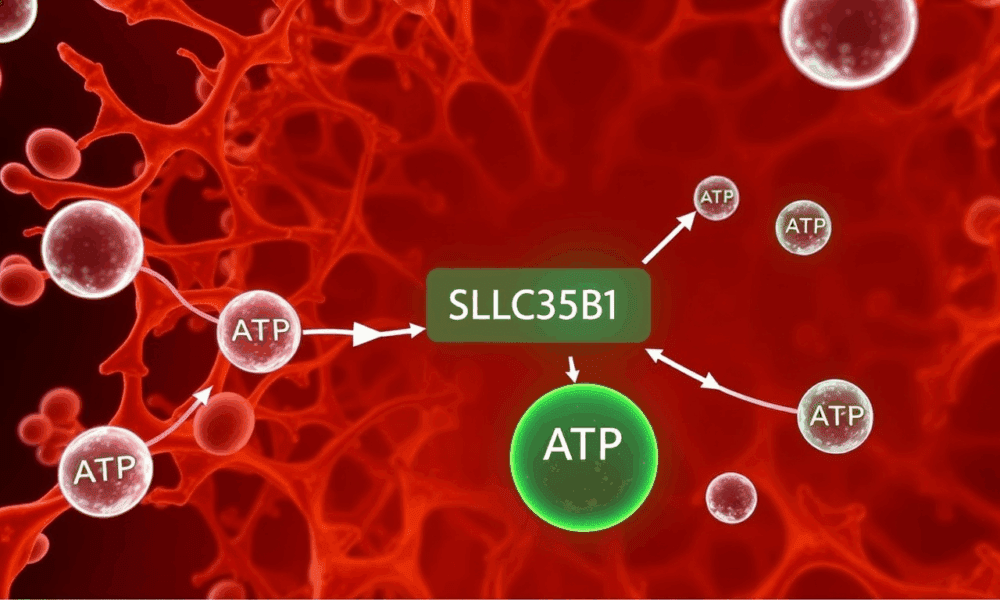
A team of scientists has answered a long-standing question in cell biology, uncovering how the cell's main energy currency, ATP, is transported into the endoplasmic reticulum...



Research reveals that for C. elegans worms, the presence of dead members of their species has profound behavioral and physiological effects, leading them to more quickly...
Cancer cells respond to stress with greater diversity. Drugs that affect DNA replication, or radiation that causes direct DNA damage, lead to increasingly diverse offspring over...


New research has shed light on how plants precisely control their growth and development, revealing that seemingly similar molecular components fulfill surprisingly different jobs.

Proteins are among the most studied molecules in biology, yet new research shows they can still hold surprising secrets. Researchers have discovered previously undetected chemical bonds...
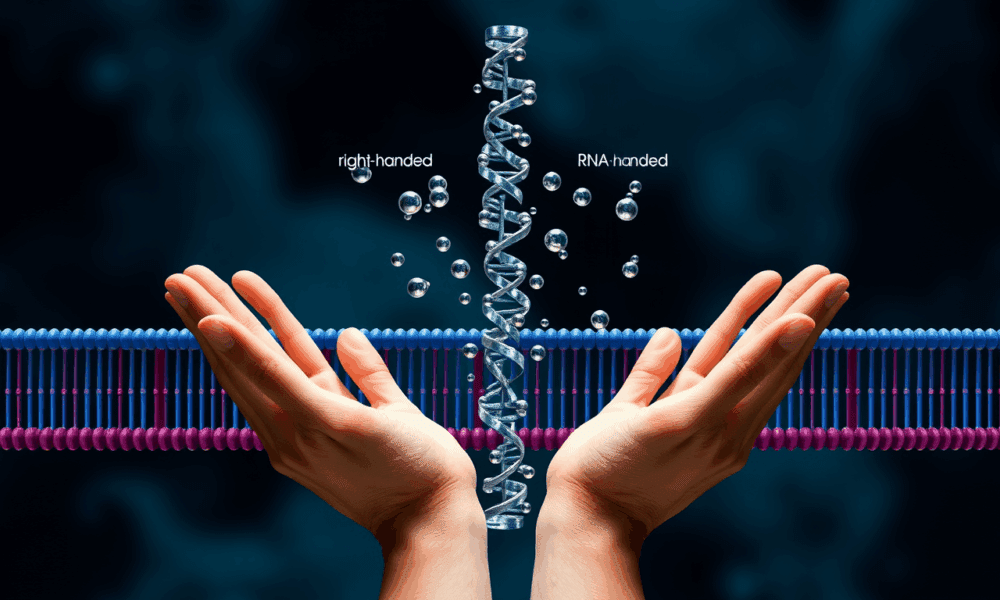
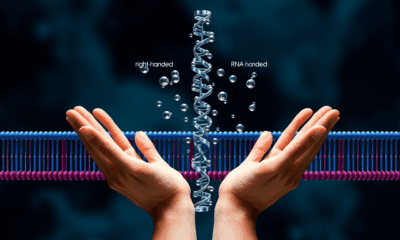

A team of researchers studied the properties of membranes to understand how these cellular structures influenced the chemistry of life on Earth as it began.
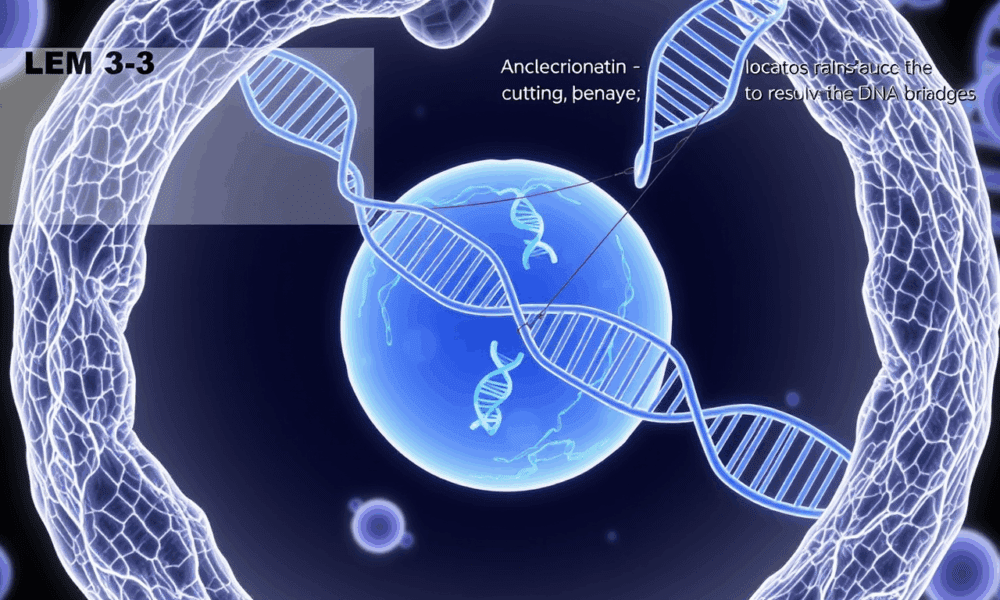



Scientists have elucidated the molecular mechanism by which LEM-3 cuts DNA bridges during cytokinesis.