

New research from the University of Sydney sheds light on how coronaviruses emerge in bat populations, focusing on young bats as hotspots for infections and co-infections...

What if mRNA vaccines could be made more powerful and less irritating? Scientists at the University of Pennsylvania have found a way to do just that—by...

A gene called SDR42E1 has been identified as a key player in how our bodies absorb and process vitamin D. Researchers found that disabling this gene...
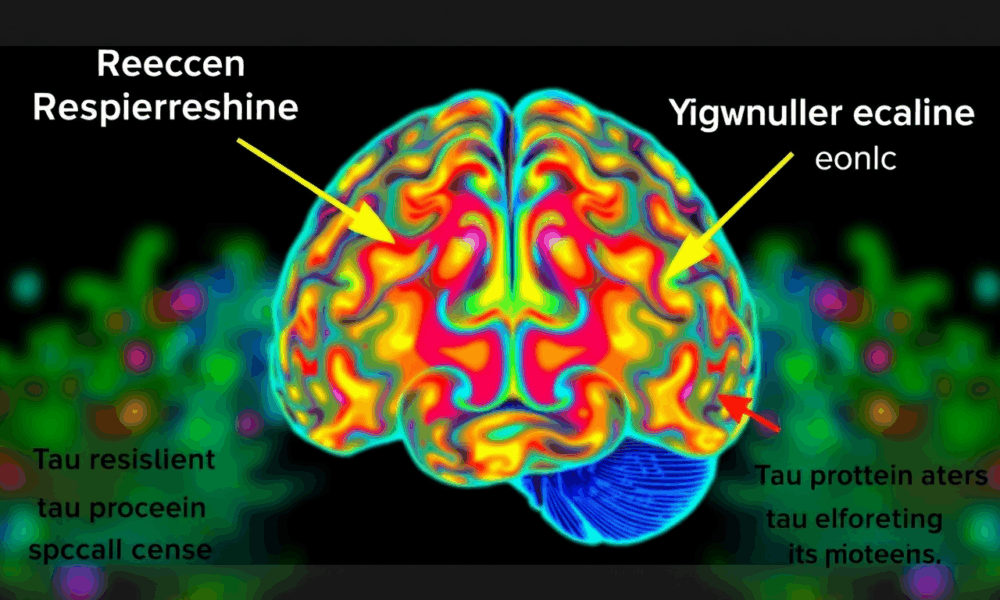
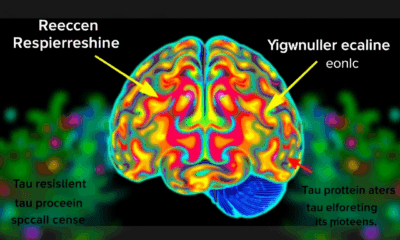
Scientists at UCSF combined advanced brain-network modeling, genetics, and imaging to reveal how tau protein travels through neural highways and how certain genes either accelerate its...
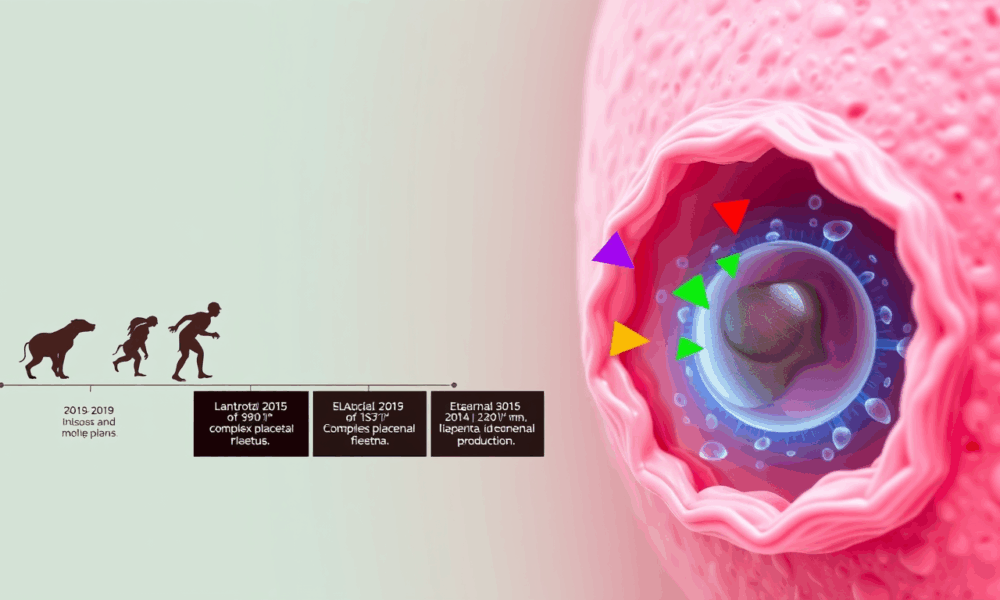
A group of scientists studying pregnancy across six different mammals—from humans to marsupials—uncovered how certain cells at the mother-baby boundary have been working together for over...



Researchers testing urine from 2- to 4-year-olds in four U.S. states uncovered 96 different chemicals, many of them unmonitored and linked to hormone and brain disruption....
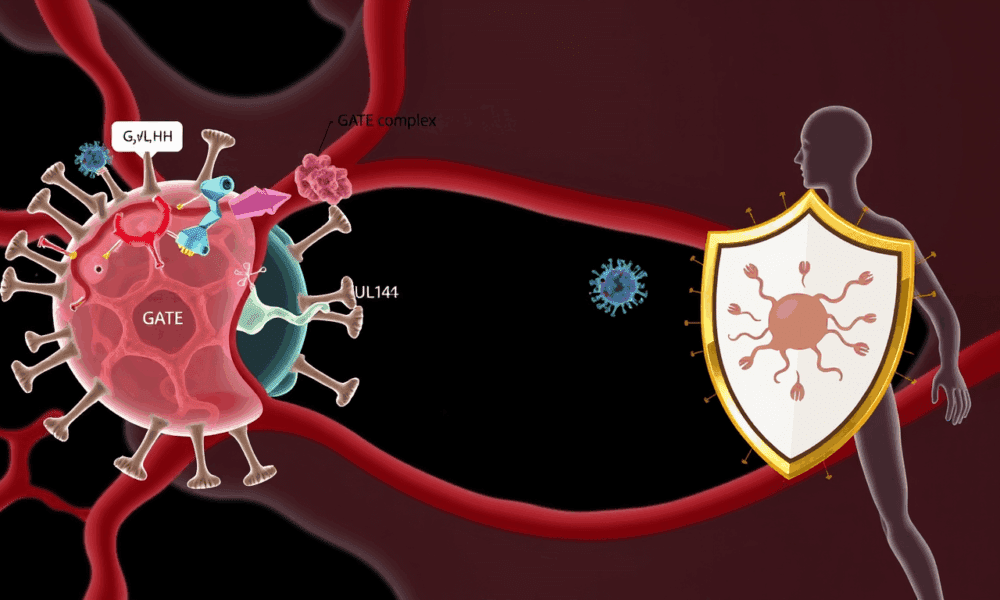
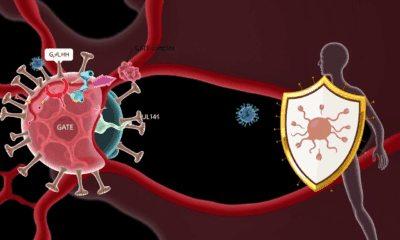

Scientists have discovered a stealthy mechanism that cytomegalovirus (CMV)—the leading infectious cause of birth defects in the U.S.—uses to infiltrate blood vessel cells while evading immune...
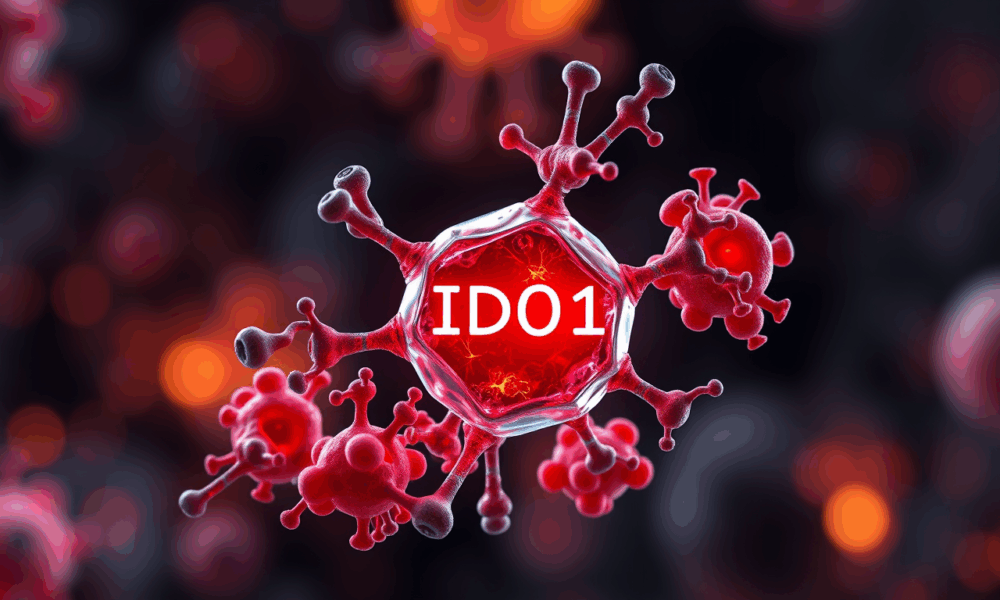

Researchers at UT Arlington have discovered a key enzyme, IDO1, that when blocked, helps immune cells regain their ability to properly process cholesterol—something that breaks down...


Leprosy’s tale stretches from 5,000-year-old skeletons in Eurasia to a startling 4,000-year-old case in Chile, revealing that the rare strain Mycobacterium lepromatosis haunted the Americas millennia...
Biological drugs have been a game-changer for people with severe asthma, helping them breathe easier and live more comfortably. But researchers at Karolinska Institutet have uncovered...