While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Dietary Supplements and Minerals
Unveiling an Ancient Mechanism of Cellular Respiration: How Primordial Microbes Breathed
A team of scientists have elucidated an ancient mechanism of cellular respiration. To that end, they studied bacteria that feed on the gases carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and turn them into acetic acid — a metabolic pathway that emerged very early in evolution. The international team has now been able to resolve the mystery of how the microbes use this process to generate energy. Their findings are also interesting for another reason: Since the microorganisms remove CO2 from their environment, they are seen as a beacon of hope in the fight against climate change.
Back and Neck Pain
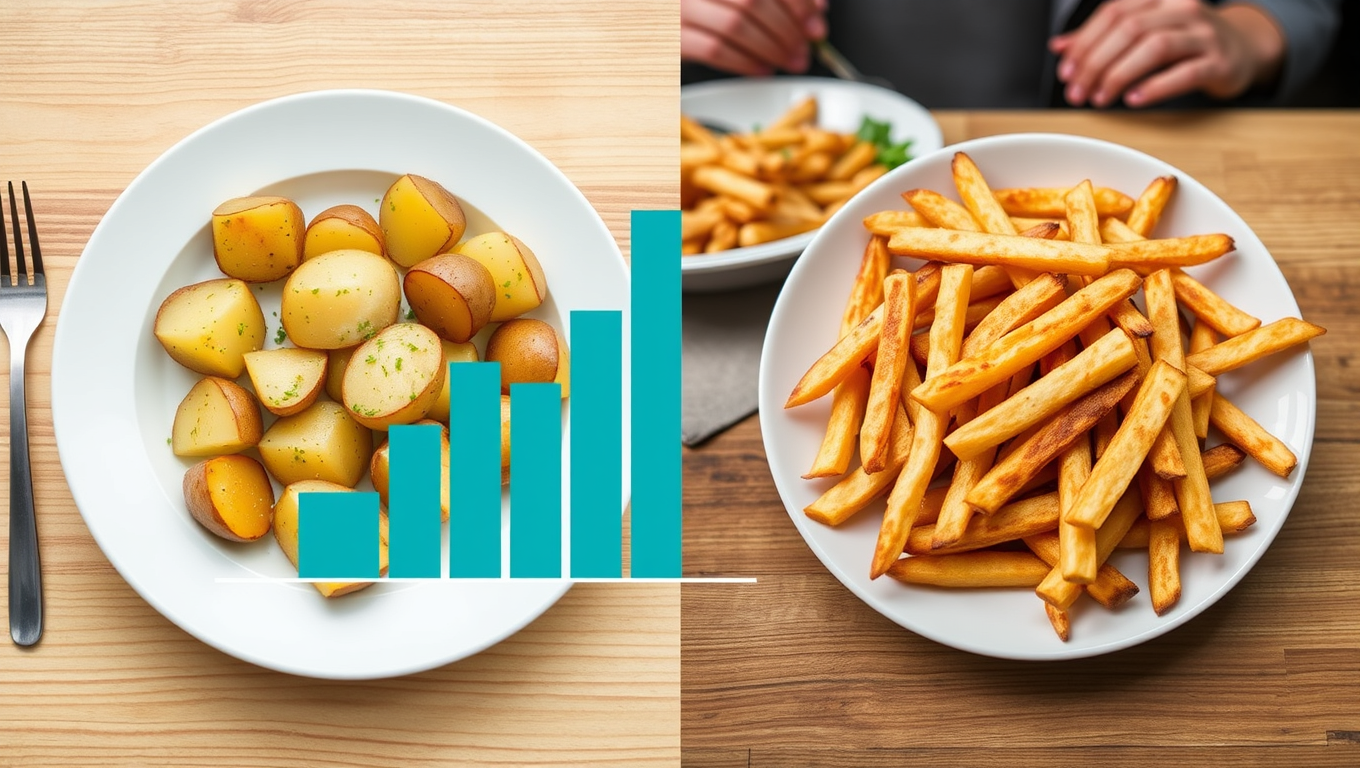
The French Fry Effect: Scientists Reveal the Surprising Truth About Potatoes and Diabetes Risk
French fries may be more than just a guilty pleasure—they could raise your risk of type 2 diabetes by 20% if eaten three times a week, while the same amount of boiled, baked, or mashed potatoes doesn’t appear to have the same effect.
Acid Rain
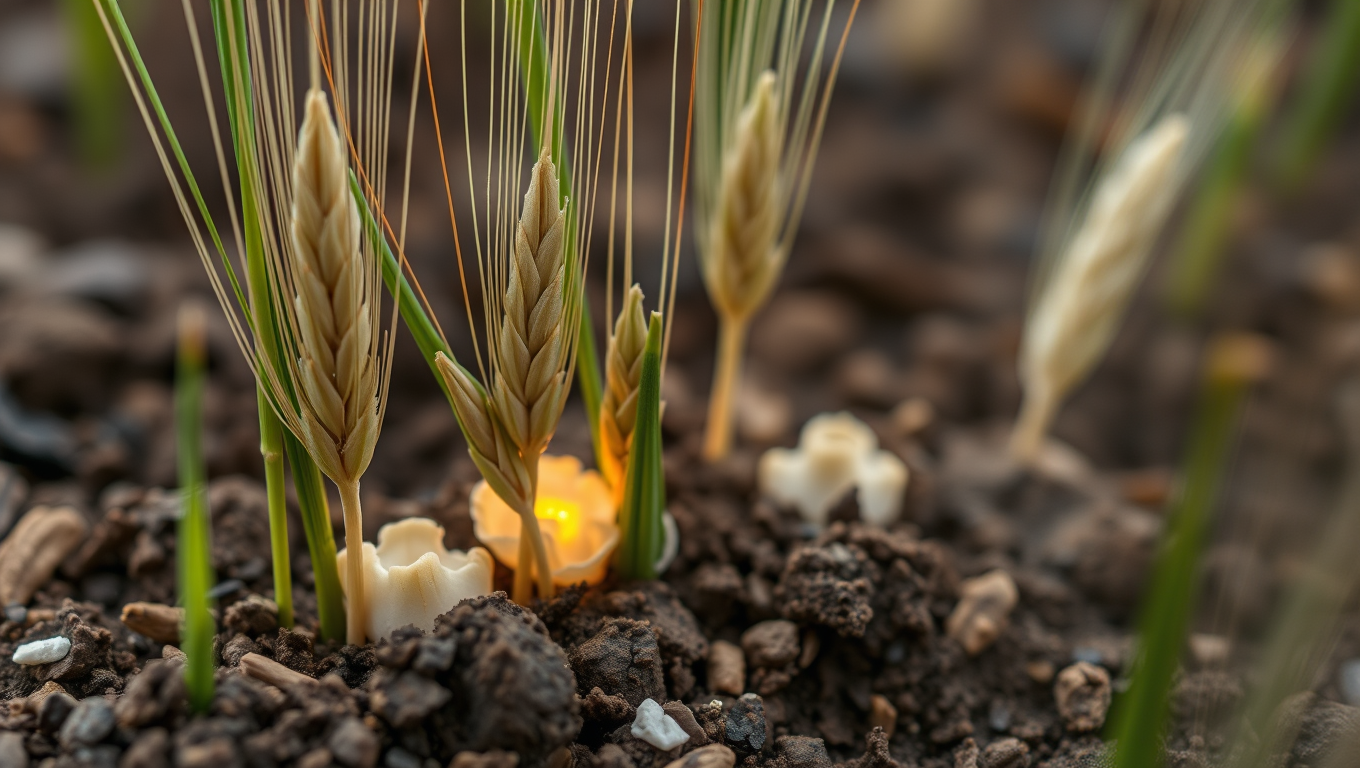
“The Fungus That Makes Bread Better: How Mycorrhizal Fungi Boost Wheat’s Nutrient Content”
Scientists have discovered that pairing bread wheat with a special soil fungus can significantly enhance its nutritional value. This partnership leads to bigger grains rich in zinc and phosphorus—without increasing anti-nutrients that block absorption. As a result, the wheat becomes a healthier option for human diets. Researchers believe this fungal strategy could offer a natural, sustainable way to fortify global crops with essential nutrients.
Accident and Trauma
“Unveiling the Invisible Killer: PM 1 Pollution Uncovered Across America”
A groundbreaking 25-year analysis using satellite technology has now mapped PM 1 levels across the U.S., uncovering how wildfires, vehicle emissions, and industrial byproducts have shaped the air we breathe. Although regulations have improved air quality over time, rising wildfire activity poses a growing challenge. This new dataset gives scientists and regulators a vital tool for targeting the most harmful pollutants and protecting public health.
-

 Detectors10 months ago
Detectors10 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer10 months ago
Cancer10 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein11 months ago
Albert Einstein11 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry10 months ago
Chemistry10 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate10 months ago
Earth & Climate10 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Agriculture and Food10 months ago
Agriculture and Food10 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions11 months ago
Diseases and Conditions11 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention