

Contrary to widespread assumptions, the largest shark that ever lived -- Otodus megalodon -- fed on marine creatures at various levels of the food pyramid and...


A gene that regulates the development of roots in vascular plants is also involved in the organ development of liverworts -- land plants so old they...


Flowers grow stems, leaves and petals in a perfect pattern again and again. A new study shows that even in this precise, patterned formation in plants,...
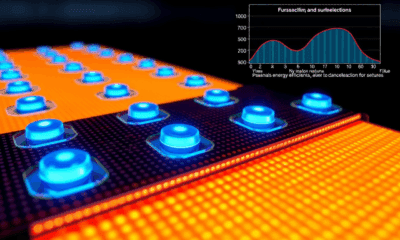
Blue phosphorescent OLEDs can now last as long as the green phosphorescent OLEDs already in devices, researchers have demonstrated, paving the way for further improving the...


As sea levels climb and weather grows more extreme, coastal regions everywhere are facing a creeping threat: salt. Salinization of freshwater and soils adversely affects 500...


New international research demonstrates global-scale patterns in how El Ni o-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) influences mangrove growth and degradation. Previously, impacts had only been documented at individual...


A new risk calculator accurately identified participants who had calcium buildup in their heart arteries and those who had a higher future heart attack risk, in...


Cold-adapted animals started to evolve 2.6 million years ago when the permanent ice at the poles became more prevalent. There followed a time when the continental...


A new study uses metabolic profiling to uncover ancient knowledge systems behind therapeutic and psychoactive plant use in ancient Arabia.


A group of fossils of elasmosaurs -- some of the most famous in North America -- have just been formally identified as belonging to a 'very...