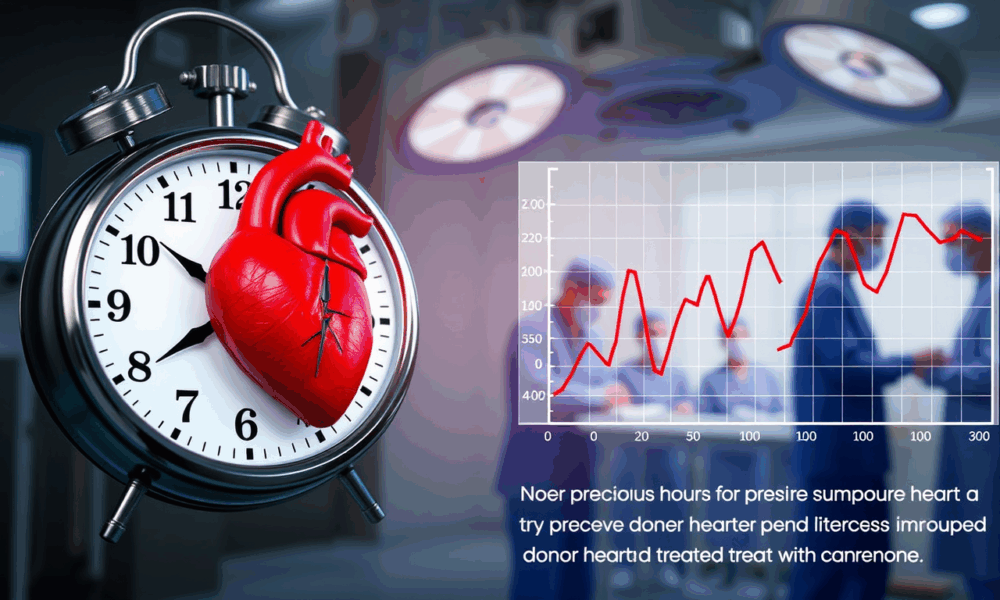

A new discovery could mean more donor hearts are available for heart transplant, giving more people a second chance at life.
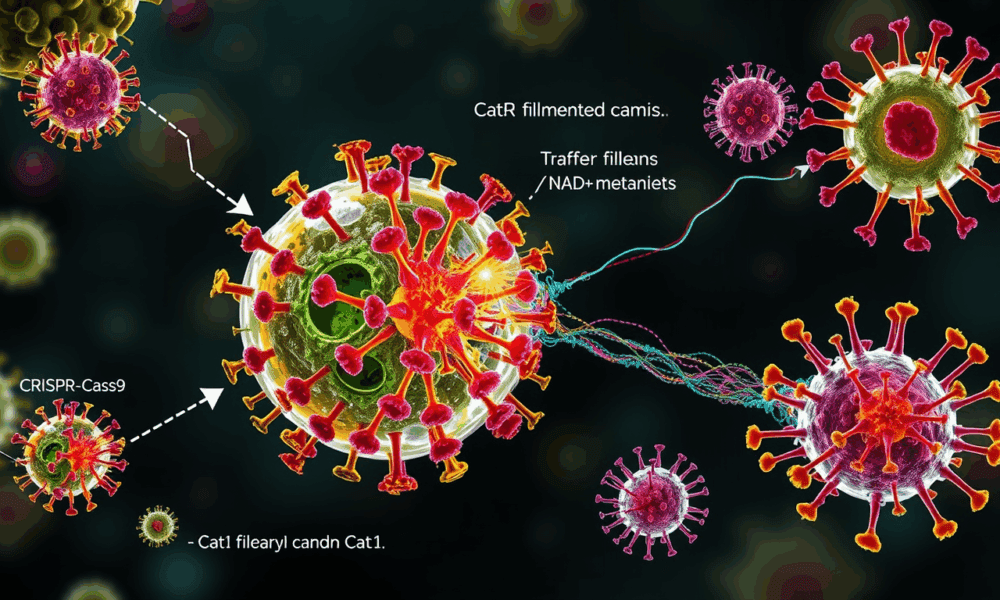
Newly discovered weapons of bacterial self-defense take different approaches to achieving the same goal: preventing a virus from spreading through the bacterial population.
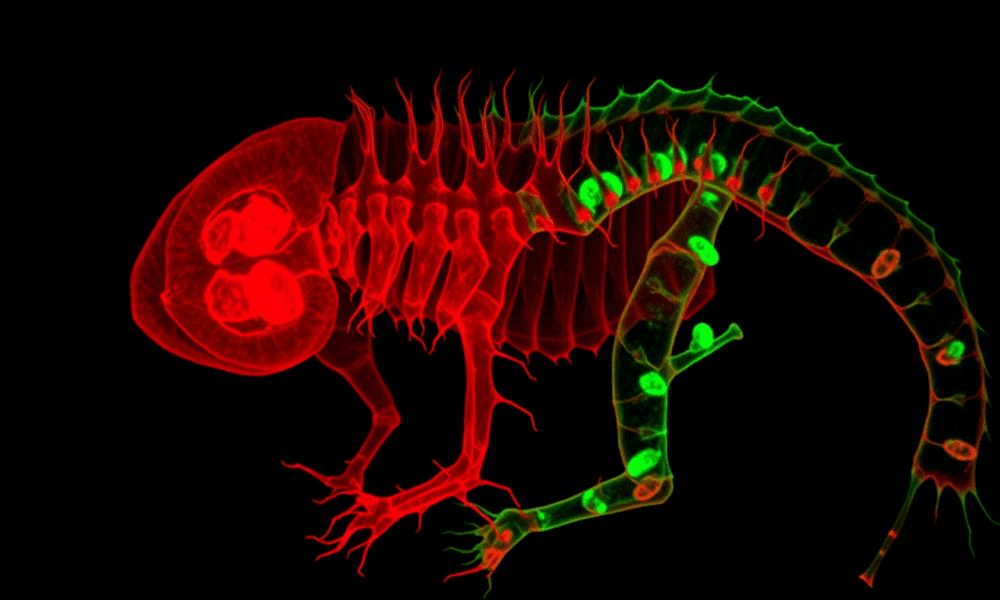
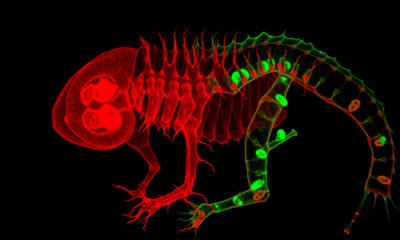
Using a new fluorescent mouse model with advanced imaging techniques, researchers have successfully visualized how musculoskeletal components are integrated into the functional locomotor system during embryonic...
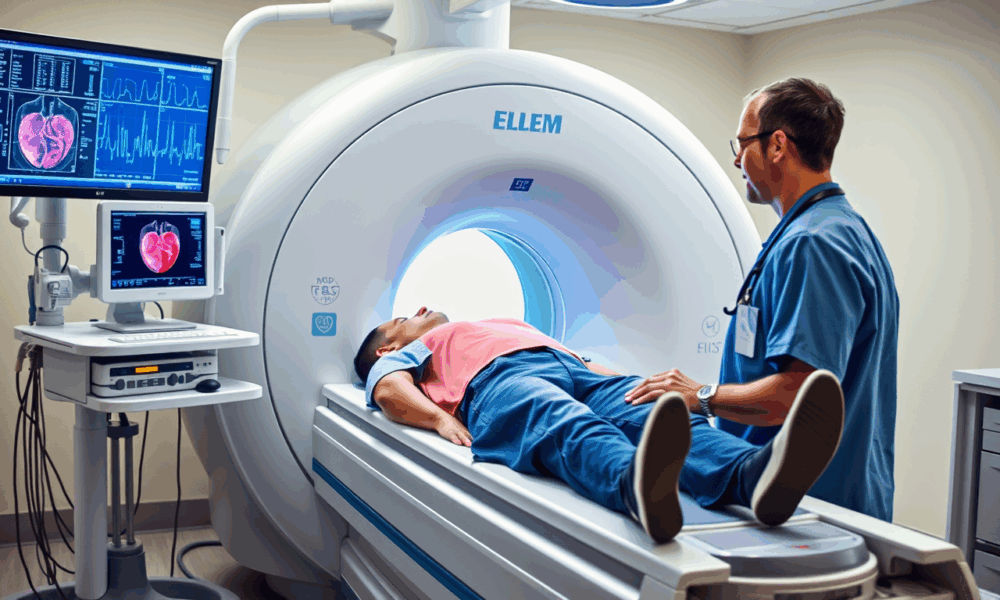
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the heart could help to detect a life-threatening heart disease and enable clinicians to better predict which patients are most...
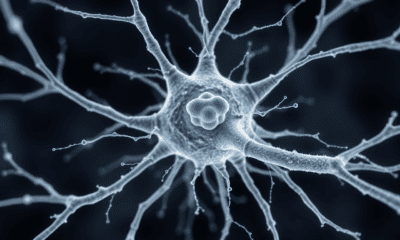
In many neurodegenerative diseases, proteins misfold and clump together in brain tissue. Scientists developed a new therapy made of peptides and a sugar that naturally occurs...



Researchers have developed a new workflow for designing enzymes from scratch, paving the way toward more efficient, powerful and environmentally benign chemistry. The new method allows...



Biologists and chemists have a new programming language to uncover previously unknown environmental pollutants at breakneck speed -- without requiring them to code.
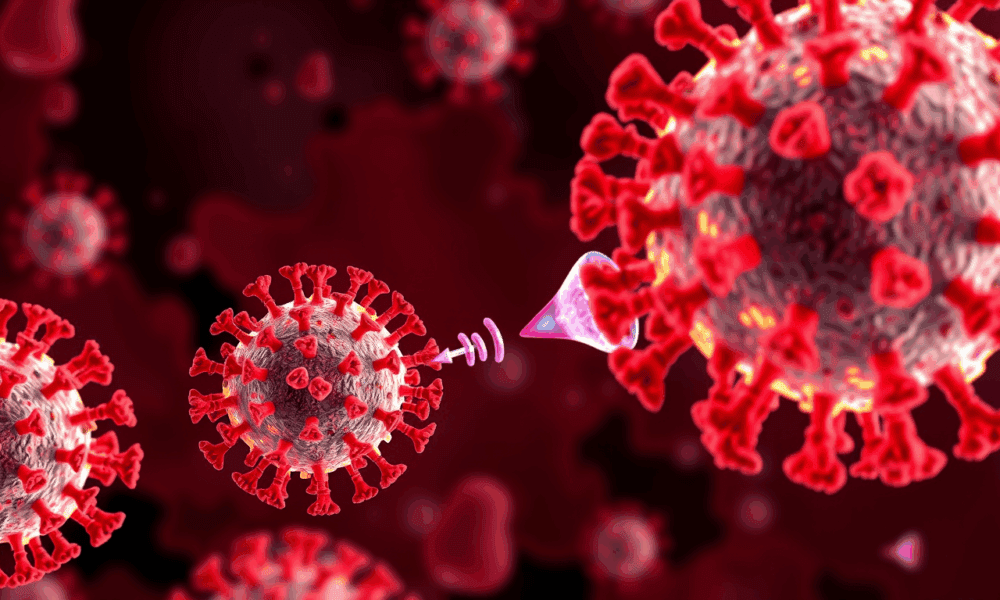
Influenza viruses are among the most likely triggers of future pandemics. A research team has developed a method that can be used to study the interaction...
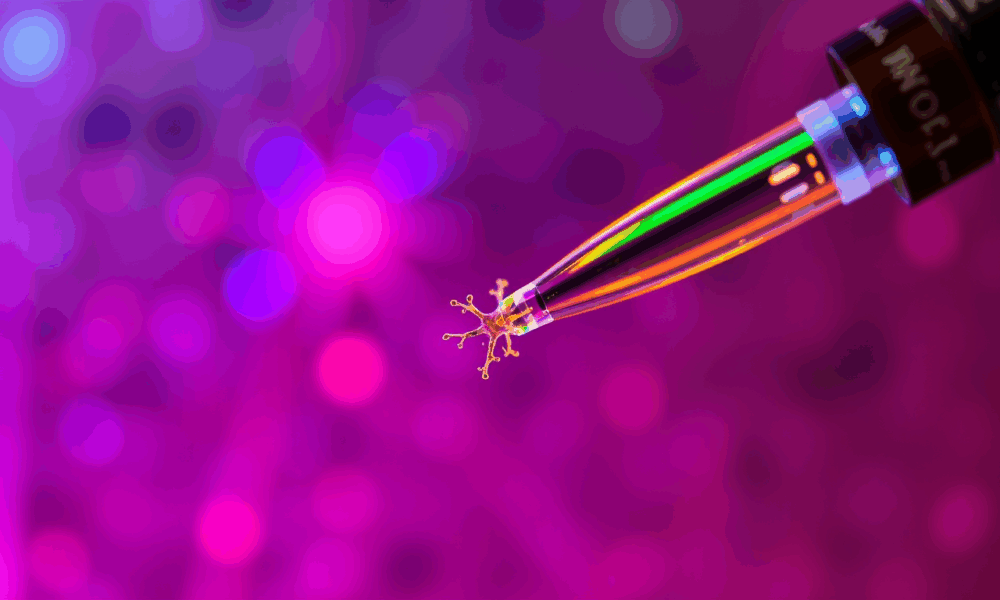



Researchers have developed a new type of pipette that can deliver ions to individual neurons without affecting the sensitive extracellular milieu. Controlling the concentration of different...
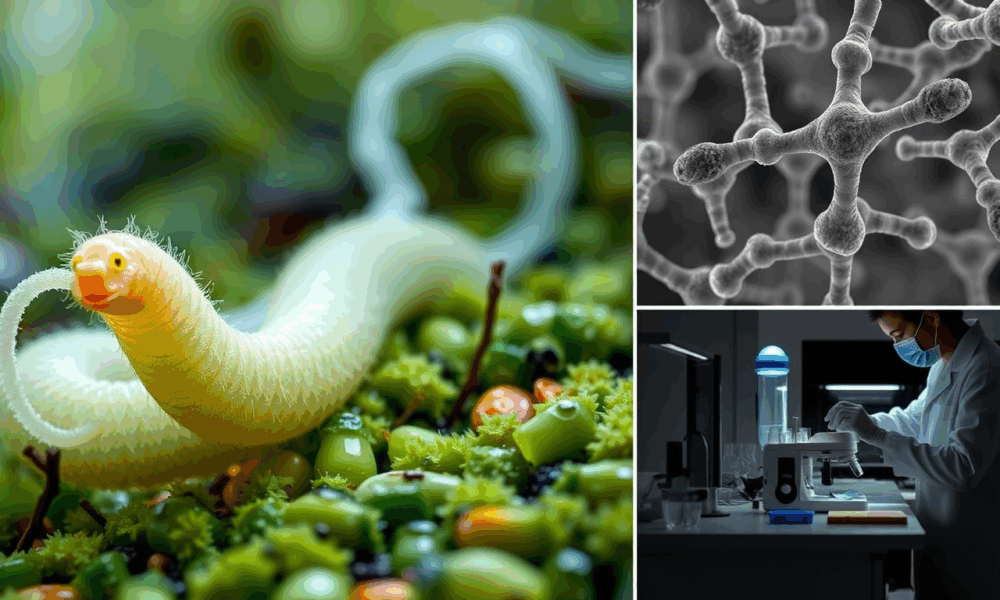



A new discovery about the slime ejected by velvet worms could revolutionize sustainable material design. The findings outline how a naturally occurring protein structure, conserved across...