


Scientists have pioneered a new way to breed climate-resilient crops faster by combining plant genebank data with climate and DNA analysis. The method, tested on sorghum,...



Researchers have discovered a protein that is involved in plant leaf aging.
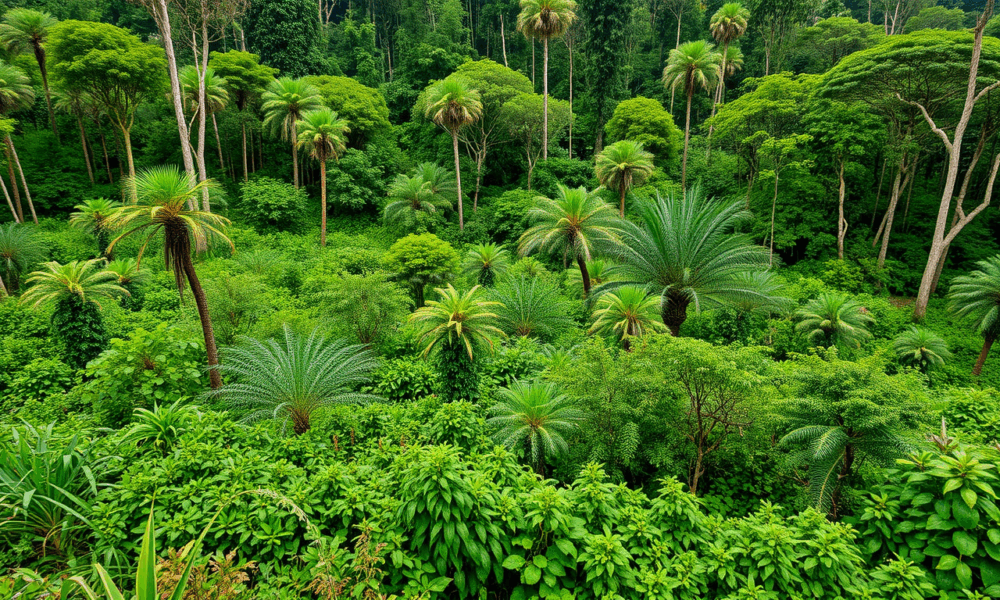



Forest-based agroforestry can restore forests, promote livelihoods, and combat climate change, but emerging agroforestry initiatives focusing only on tree planting is leading to missed opportunities to...
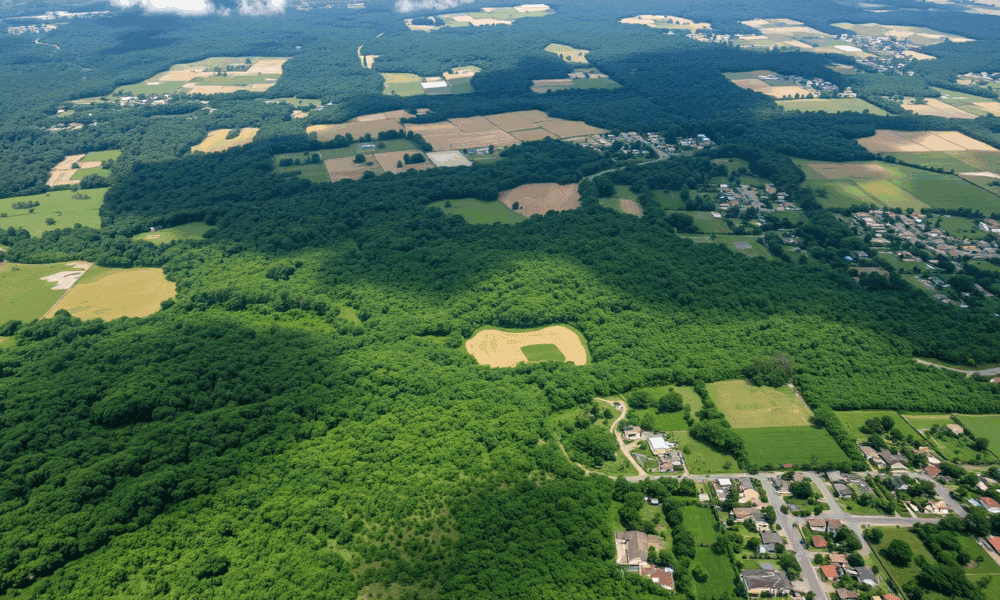



A study finds small-scale tree cover in Costa Rica boosts biodiversity while limiting dangerous mosquito species.
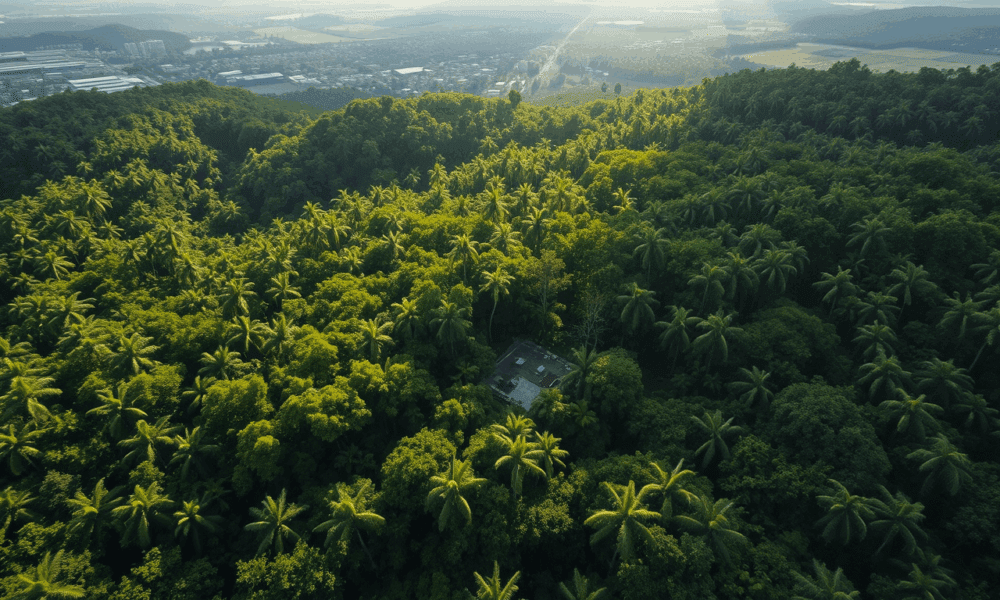



Replanting forests can help cool the planet even more than some scientists once believed, especially in the tropics. But even if every tree lost since the...
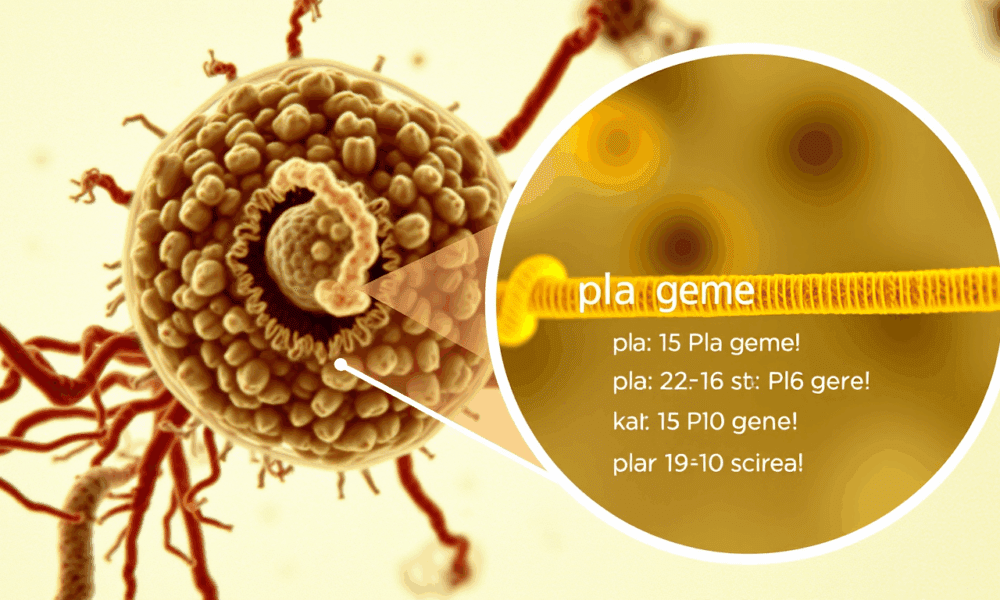

Scientists have documented the way a single gene in the bacterium that causes bubonic plague, Yersinia pestis, allowed it to survive hundreds of years by adjusting...
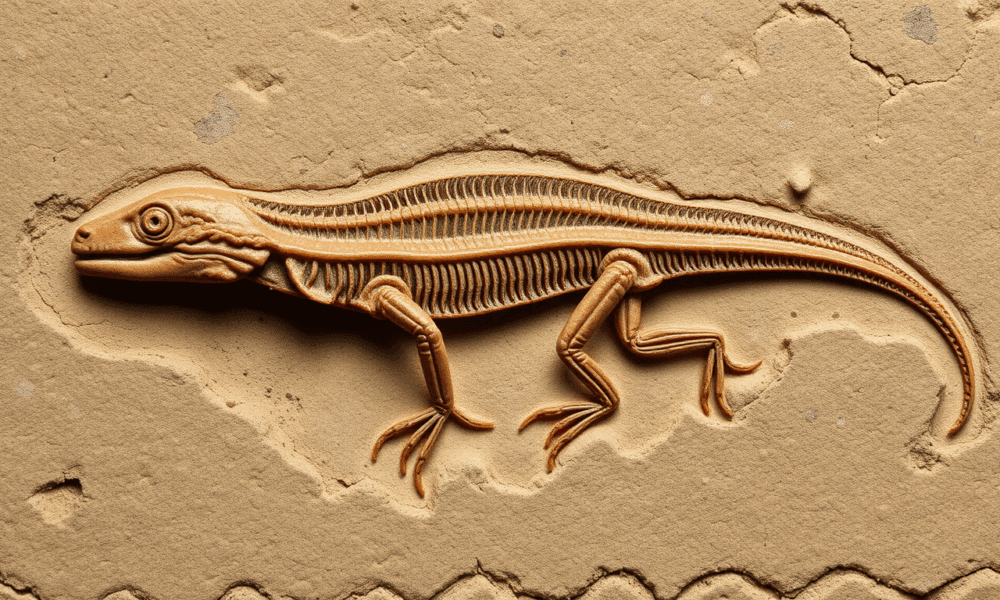



The fossils of ancient salamander-like creatures in Scotland are among the most well-preserved examples of early stem tetrapods -- some of the first animals to make...
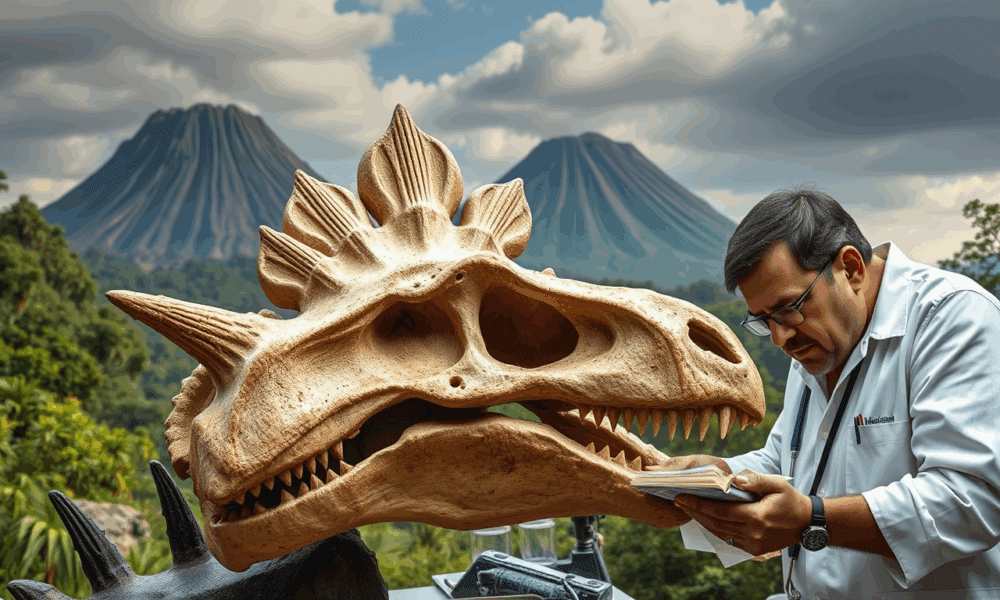


Palaeontologists have analyzed the most complete stegosaurian skull ever found in Europe and rewritten the evolutionary history of this iconic group of dinosaurs.
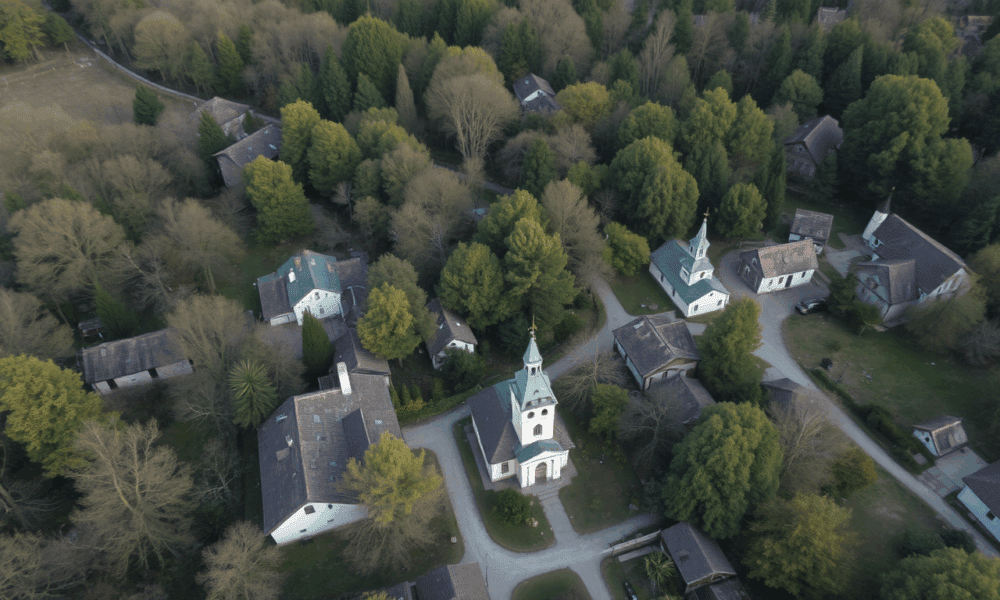



Many bat species native to Germany, such as the Leisler's bat, are forest specialists. However, as it is becoming increasingly hard for them to find tree...
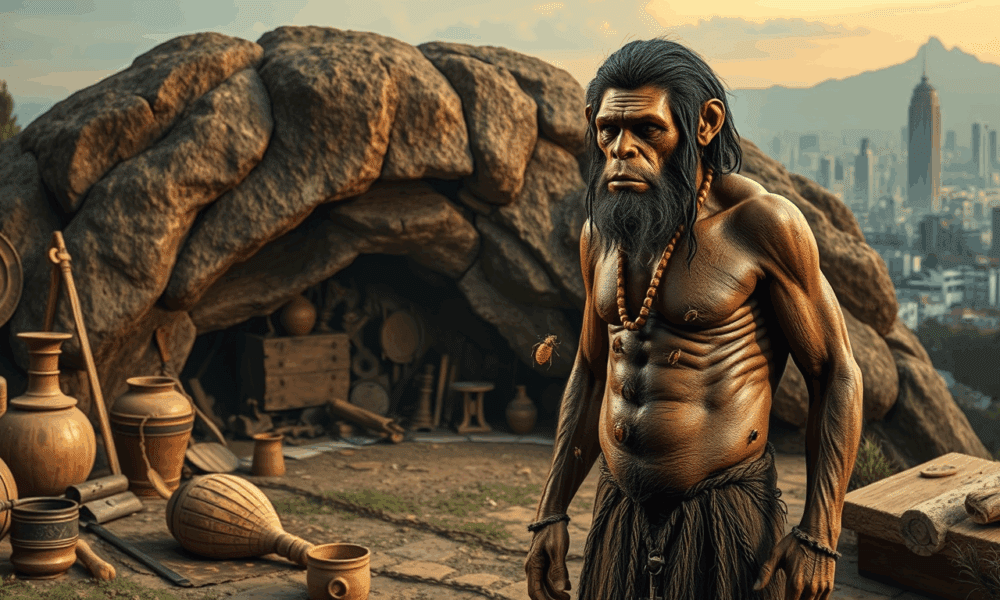

Researchers compared the whole genome sequence of two genetically distinct lineages of bed bug, and their findings indicate bed bugs may well be the first true...