While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Atmosphere
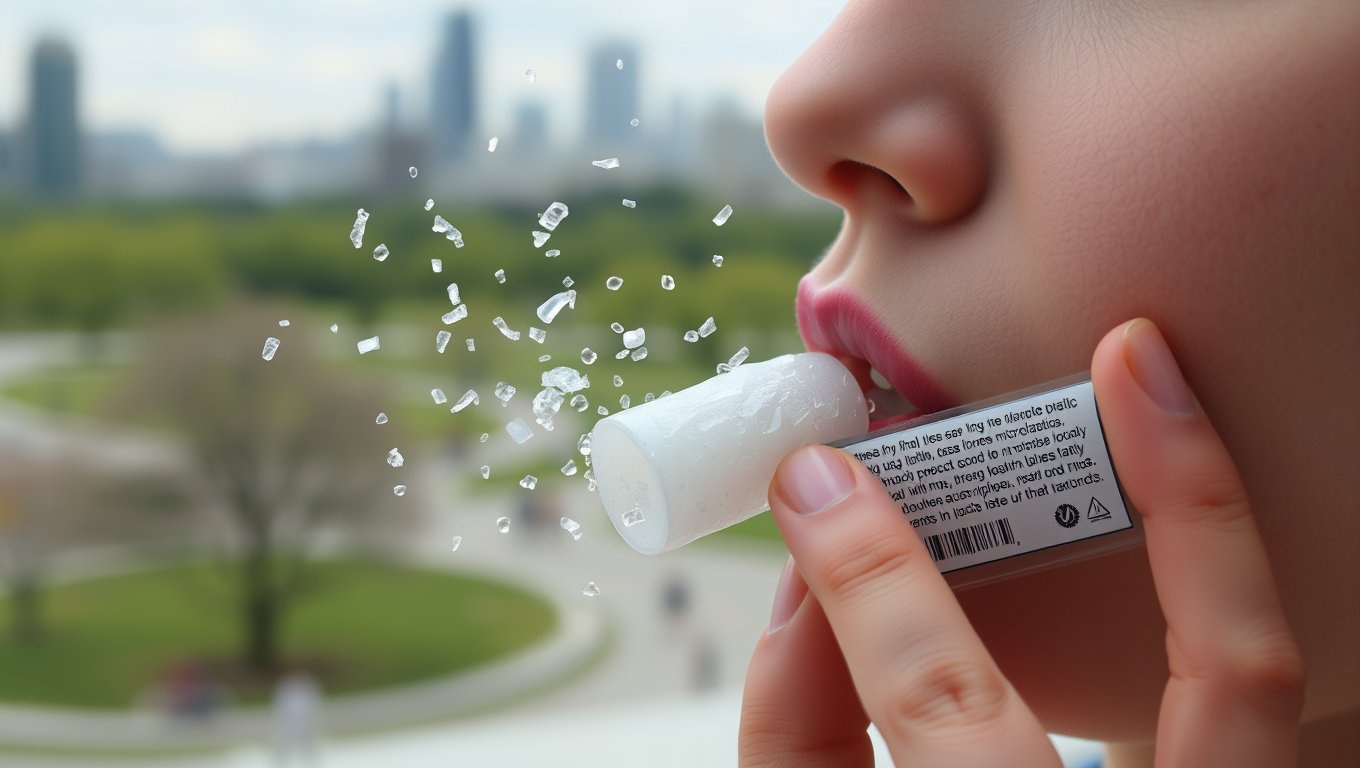
“Chewing Gum: A Hidden Source of Microplastics in Your Saliva”
Plastic is everywhere in our daily lives. And much of what we use, such as cutting boards, clothes and cleaning sponges, can expose us to tiny, micrometer-wide plastic particles called microplastics. Now, chewing gum could be added to the list. In a pilot study, researchers found that chewing gum can release hundreds to thousands of microplastics per piece into saliva and potentially be ingested.

Atmosphere
NASA’s SWOT Satellite Captures Kamchatka Megaquake Tsunami in Stunning Detail
When a massive 8.8 magnitude earthquake struck off Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula, NASA and CNES’s SWOT satellite captured a rare and detailed picture of the tsunami that followed. Recorded just over an hour after the quake, the satellite revealed the wave’s height, shape, and path, offering scientists an unprecedented multidimensional view from space.
Atmosphere
Unpacking America’s Winter Puzzle: How the Stratosphere Shapes Extreme Cold Snaps
Even in a warming climate, brutal cold snaps still hammer parts of the U.S., and a new study uncovers why. High above the Arctic, two distinct polar vortex patterns — both distorted and displaced — play a major role in steering icy air toward different regions. One sends it plunging into the Northwest, while the other aims it at the Central and Eastern U.S. Since 2015, the westward version has been more common, bringing intensified cold to the Northwest in defiance of global warming trends. This stratospheric detective work offers fresh insight into extreme winter weather — and could supercharge long-range forecasts.
Atmosphere
Uncovering the Hidden Link: NASA Discovers Connection Between Earth’s Core and Life-Sustaining Oxygen
For over half a billion years, Earth’s magnetic field has risen and fallen in sync with oxygen levels in the atmosphere, and scientists are finally uncovering why. A NASA-led study reveals a striking link between deep-Earth processes and life at the surface, suggesting that the planet’s churning molten interior could be subtly shaping the conditions for life. By comparing ancient magnetic records with atmospheric data, researchers found that these two seemingly unrelated phenomena have danced together since the Cambrian explosion, when complex life first bloomed. This tantalizing connection hints at a single, hidden mechanism — perhaps even continental drift — orchestrating both magnetic strength and the air we breathe.
-

 Detectors10 months ago
Detectors10 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer11 months ago
Cancer11 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein11 months ago
Albert Einstein11 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry10 months ago
Chemistry10 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Agriculture and Food11 months ago
Agriculture and Food11 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions11 months ago
Diseases and Conditions11 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention