While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Cold and Flu
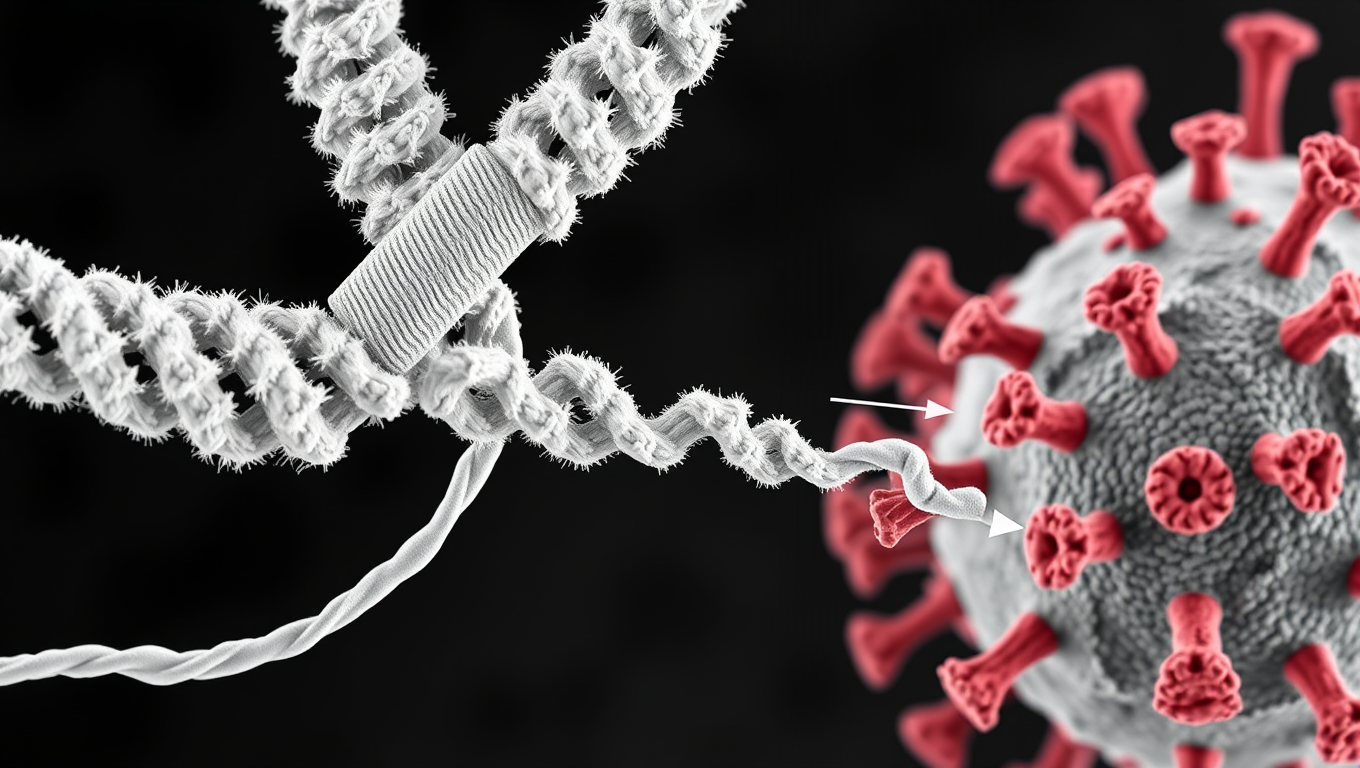
Scientists Discover Llama Antibodies That Shut Down COVID-19 and Its Future Variants
Powerful llama-derived antibodies could be the key to stopping not just current SARS viruses, but future ones too. Scientists have discovered a unique class of nanobodies that clamp the coronavirus spike protein shut at a highly conserved region, rendering it unable to infect cells. Unlike existing therapies that target mutating regions, this approach strikes at the virus s core machinery, giving it little room to evolve. Even when pushed to mutate, the virus faltered, making this a high-potential strategy for broad, lasting protection.
Cold and Flu
“Unlocking the Mystery: Scientists Discover How to Break Down Brain Cell Clumps and Develop New Treatment”
Scientists have discovered how harmful clumps inside brain cells—linked to diseases like ALS and Huntington’s—form, and found a way to break them apart. These sticky tangles of RNA develop inside tiny liquid-like droplets in cells and can linger long after their surroundings vanish. By introducing a special protein, the team could stop the clumps from forming, and with a custom-designed piece of RNA, they could even dissolve them.
Allergy
Flossing for Vaccines: A New Method to Deliver Immunizations
Scientists have discovered that flossing between your teeth could one day help vaccinate you. By targeting a uniquely permeable gum tissue called the junctional epithelium, this new method stimulates immunity right where many infections enter: the mouth, nose, and lungs. Using dental floss on mice to apply a flu vaccine triggered a robust immune response—better than existing oral approaches and comparable to nasal vaccines, but without the risks. It even worked with mRNA and protein-based vaccines.
Alternative Medicine
A Sweet Breakthrough: How a Sugar Molecule Could Help Treat Type 1 Diabetes
In a fascinating twist, Mayo Clinic researchers discovered that a sugar molecule cancer cells use to hide from the immune system might also protect insulin-producing beta cells in type 1 diabetes. By engineering these cells with the same sugar molecule—sialic acid—they prevented immune attacks in lab models. This approach could lead to better transplant options without broad immune suppression, offering hope for millions living with the autoimmune disease.
-

 Detectors10 months ago
Detectors10 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate12 months ago
Earth & Climate12 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer11 months ago
Cancer11 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein12 months ago
Albert Einstein12 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry11 months ago
Chemistry11 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Diseases and Conditions12 months ago
Diseases and Conditions12 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention
-

 Agriculture and Food11 months ago
Agriculture and Food11 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”