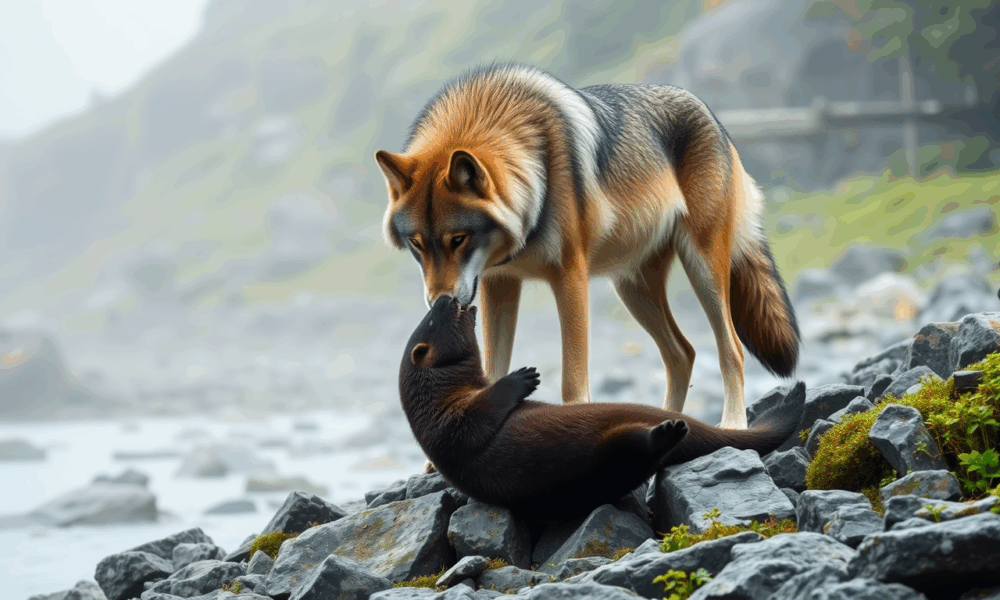



Scientists show that wolves that are eating sea otters in Alaska have much higher concentrations of mercury than those eating other prey such as deer and...



A pioneering method to simulate how microscopic particles move through the air could boost efforts to combat air pollution, a study suggests.
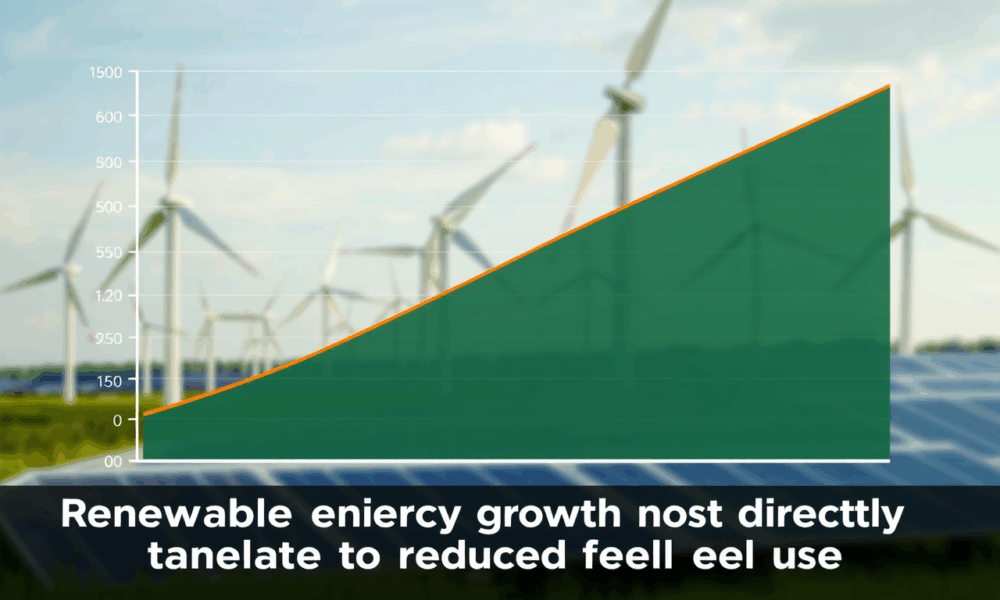

Increasing renewable energy may not reduce the use of fossil fuels in the United States, according to a new study .
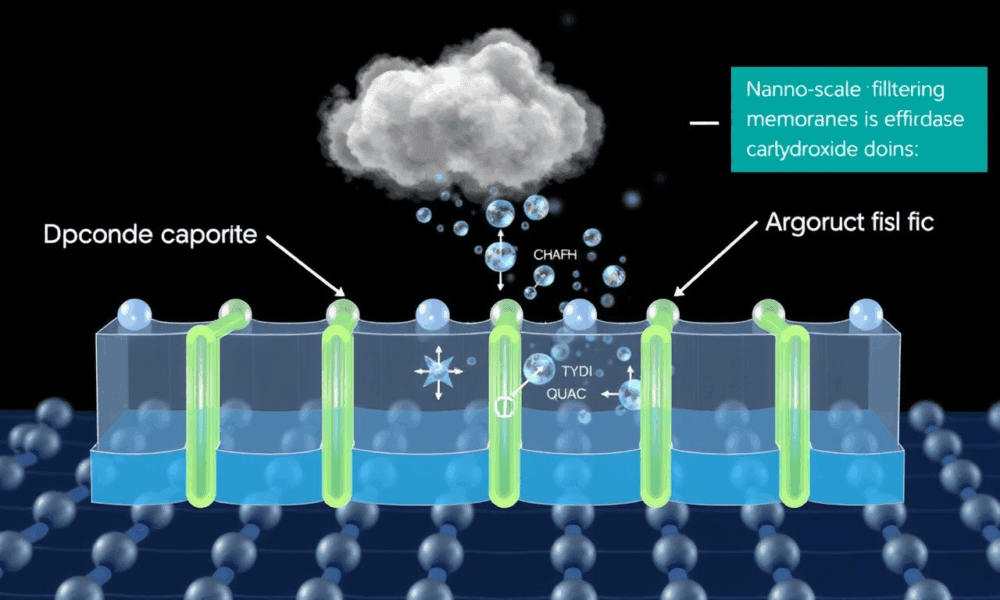

New research could improve the efficiency of electrochemical carbon-dioxide capture and release by six times and cut costs by at least 20 percent. Researchers added nanoscale...


The average energy project costs 40% more than expected for construction and takes almost two years longer than planned, finds a new global study. One key...
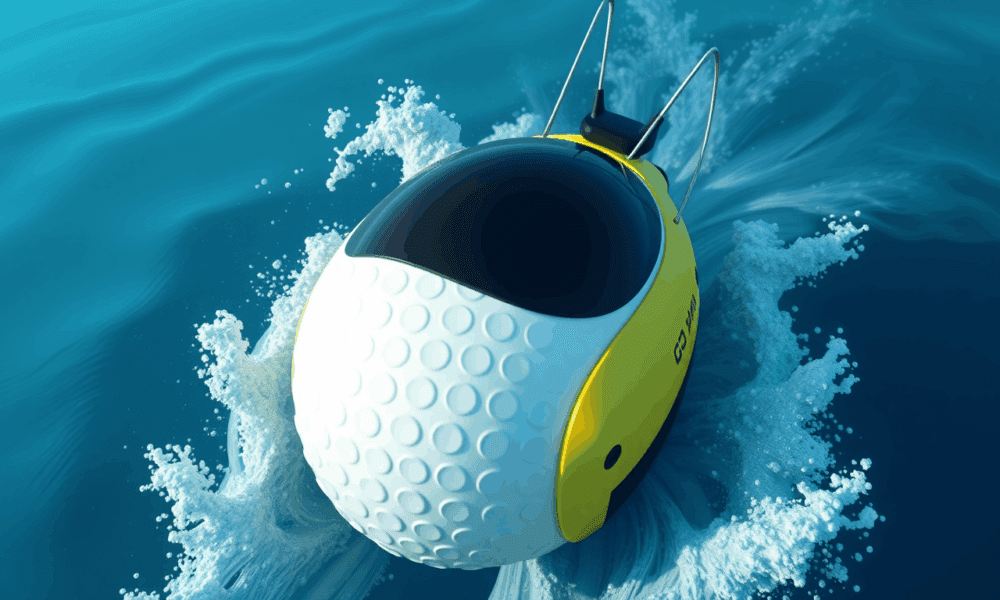



Underwater or aerial vehicles with dimples like golf balls could be more efficient and maneuverable, a new prototype has demonstrated.
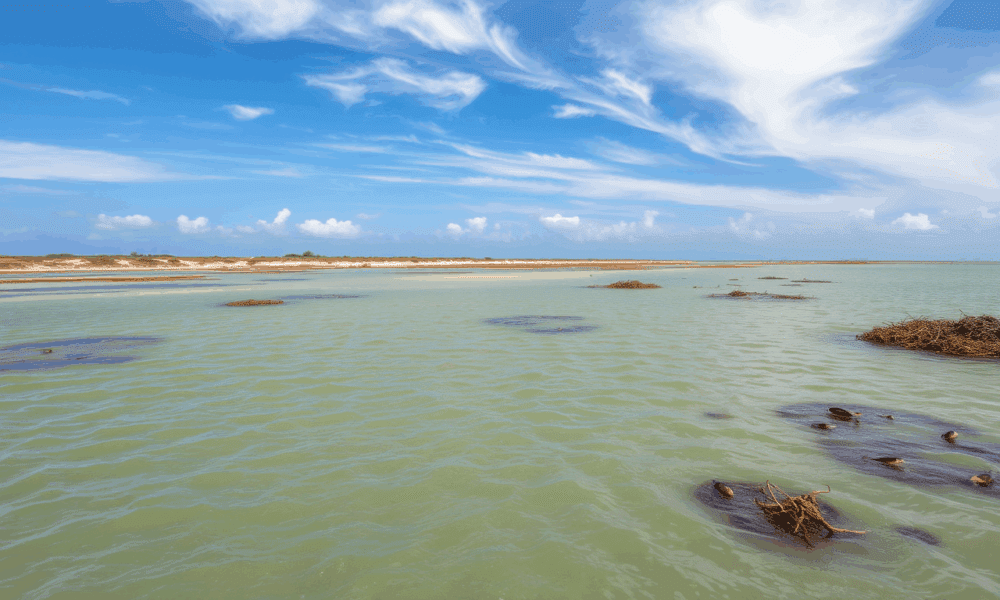



The impacts of human activity and climate change are coalescing to make coastal lagoons saltier, changing the microbial life they support and the function they play...



Stifling heat and sticky air often make summertime in the city uncomfortable. Due to the heat island effect, urban areas are significantly warmer than nearby rural...



A team of researchers has developed a new strategy for identifying hazardous pollutants in soil -- even ones that have never been isolated or studied in...


Researchers have developed two unique energy-efficient and cost-effective systems that use urea found in urine and wastewater to generate hydrogen. The unique systems reveal new pathways...