


Chemists have demonstrated how RNA (ribonucleic acid) might have replicated itself on early Earth -- a key process in the origin of life.

A new study finds that chronic cannabis use -- whether it's smoked or consumed in edible form -- is associated with significant cardiovascular risks.
In a major leap forward for genetic and biomedical research, scientists have developed a powerful new artificial intelligence tool that can predict the 3D shape of...
A team identified herpes virus saimiri, which infects the T cells of squirrel monkeys, as a source of proteins that activate pathways in T cells that...
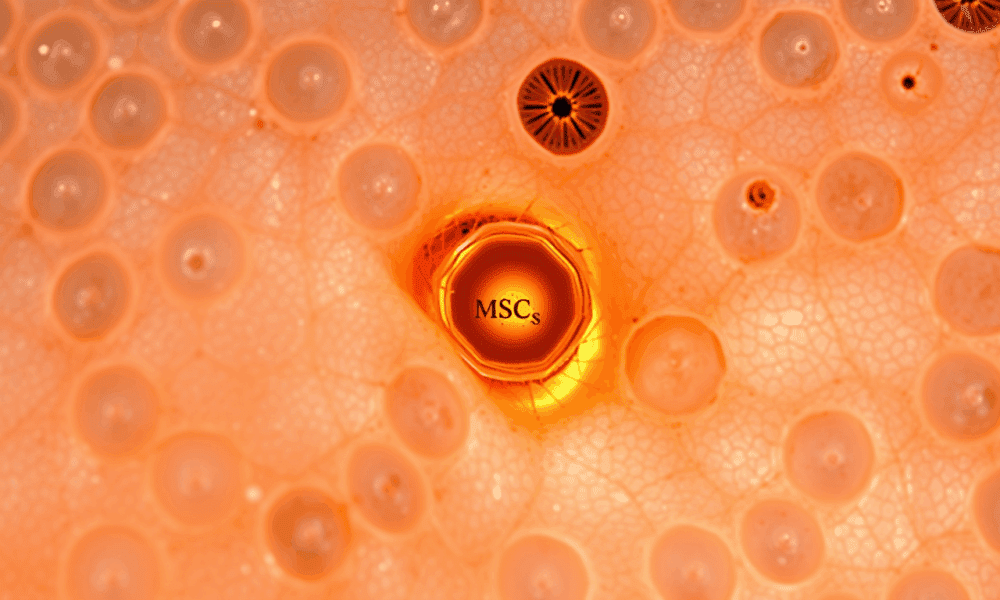
Scientists have discovered cells in the skin of Atlantic salmon that offer new insights into how wounds heal, tissues regenerate, and cellular transitions support long-term skin...



Alterations to the diet of pests could impact how quickly they can adapt to biopesticides.

In biology, enzymes have evolved over millions of years to drive chemical reactions. Scientists have now derived universal rules to enable the de novo design of...

A new study proves that a type of genetic element called 'introners' are the mechanism by which many introns spread within and between species, also providing...



Research reveals that for C. elegans worms, the presence of dead members of their species has profound behavioral and physiological effects, leading them to more quickly...



With its fascinating ability to regrow entire limbs and internal organs, the Mexican axolotl is the ideal model for studying regeneration. Scientists have now found a...