


Neanderthals living just 70 kilometers apart in Israel may have had different food prep customs, according to new research on butchered animal bones. These subtle variations...



After baffling scholars for over a century, Cambridge researchers have reinterpreted the long-lost Song of Wade, revealing it to be a chivalric romance rather than a...



For centuries, we’ve imagined Neanderthals as distant cousins — a separate species that vanished long ago. But thanks to AI-powered genetic research, scientists have revealed a...



A major breakthrough in Maya archaeology has emerged from Caracol, Belize, where the University of Houston team uncovered the tomb of Te K'ab Chaak—Caracol’s first known...


Scientists have uncovered DNA from 214 ancient pathogens in prehistoric humans, including the oldest known evidence of plague. The findings show zoonotic diseases began spreading around...
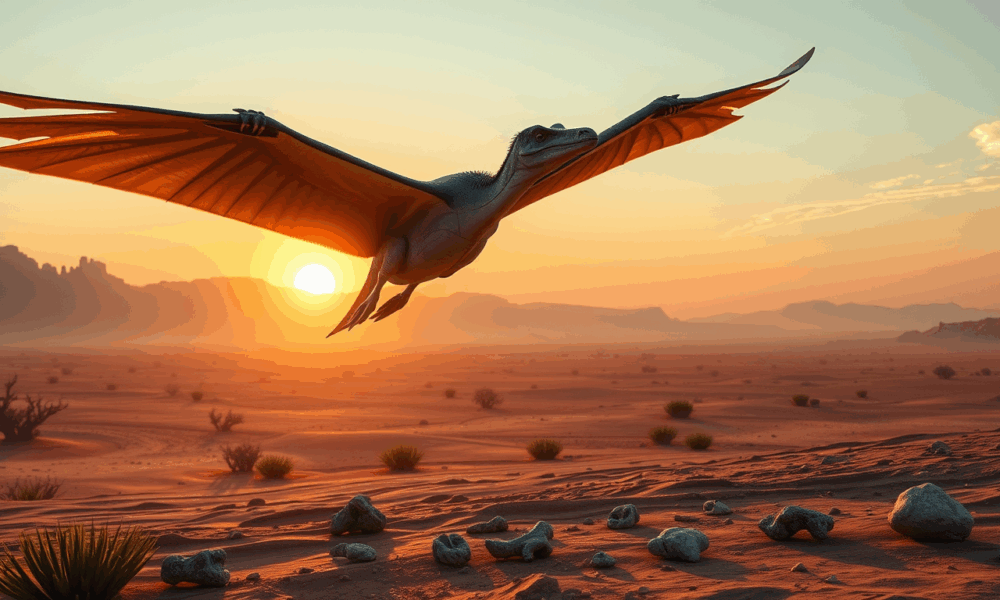



In the remote reaches of Arizona s Petrified Forest National Park, scientists have unearthed North America's oldest known pterosaur a small, gull-sized flier that once soared...
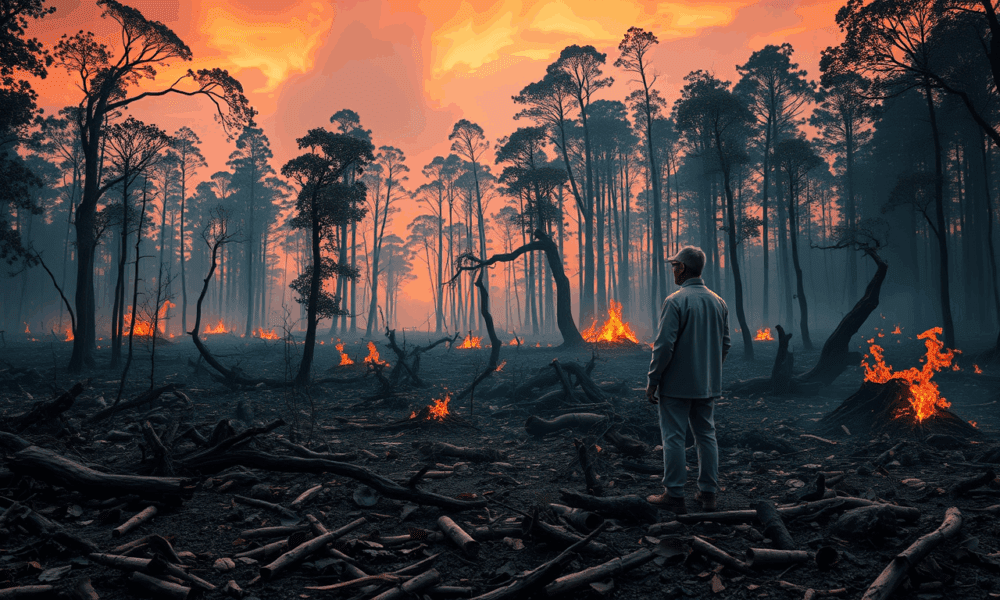



When Siberian volcanoes kicked off the Great Dying, the real climate villain turned out to be the rainforests themselves: once they collapsed, Earth’s biggest carbon sponge...
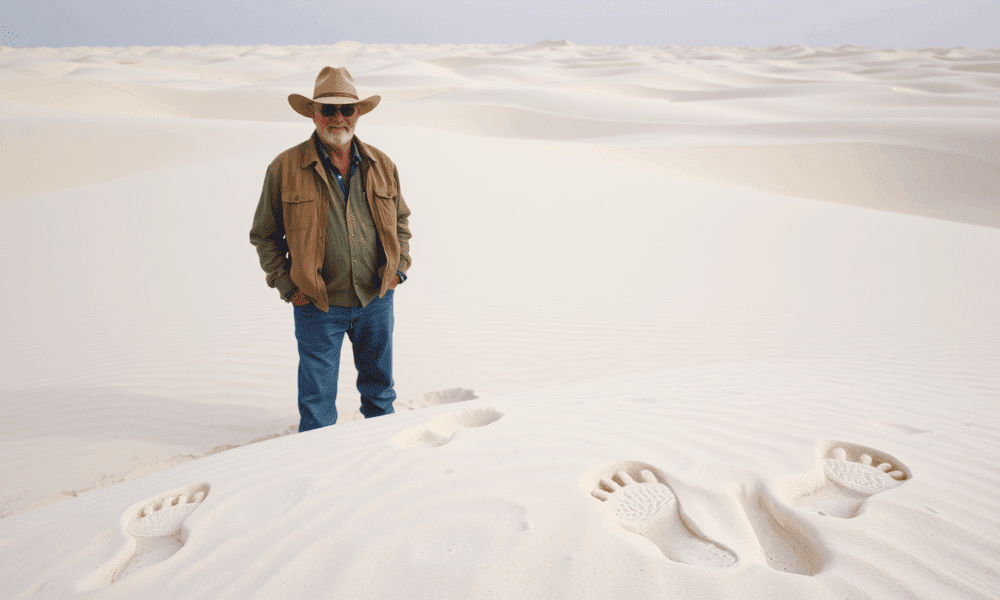



Footprints found in the ancient lakebeds of White Sands may prove that humans lived in North America 23,000 years ago — much earlier than previously believed....
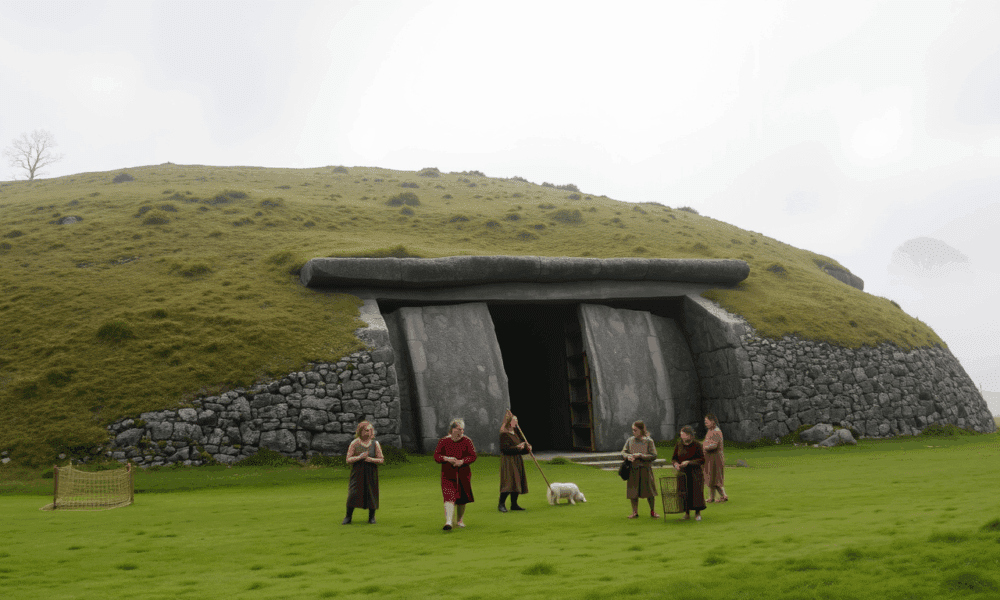



DNA from a skull found at Newgrange once sparked theories of a royal incestuous elite in ancient Ireland, but new research reveals no signs of such...


A massive, extinct salamander with jaws like a vice once roamed ancient Tennessee and its fossil has just rewritten what we thought we knew about Appalachian...