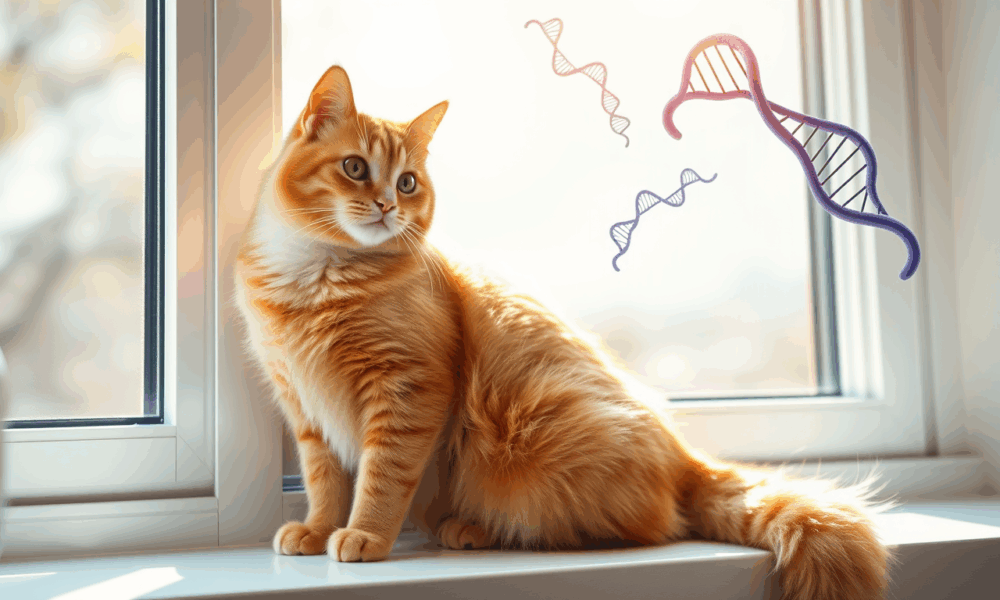



Many an orange cat-affiliated human will vouch for their cat's, let's say, specialness. But now scientists have confirmed that there is, in fact, something unique about...
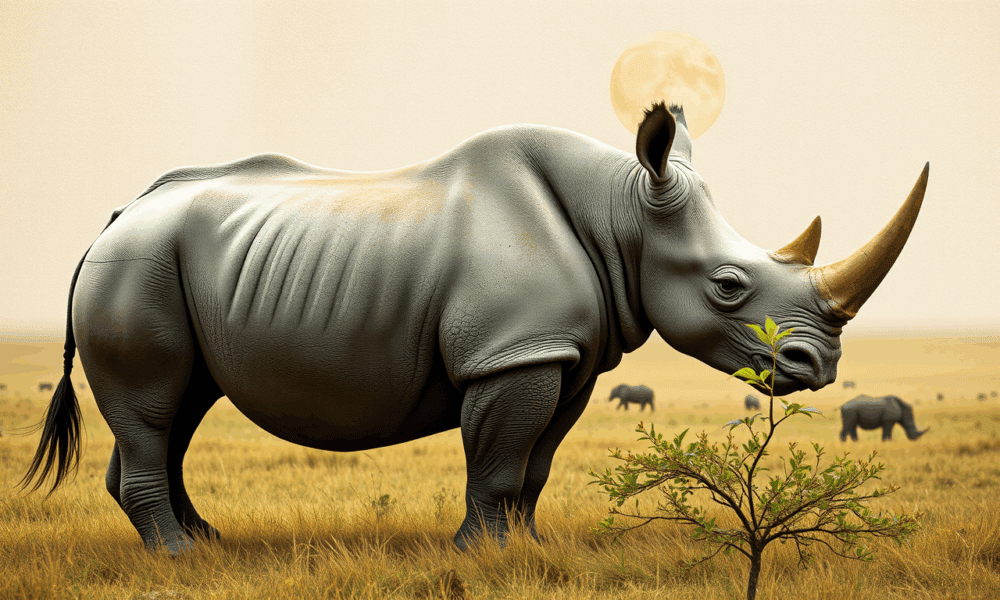



The northern white rhinoceros is one of the rarest animals on Earth, with just two females left and no natural way for the species to reproduce....
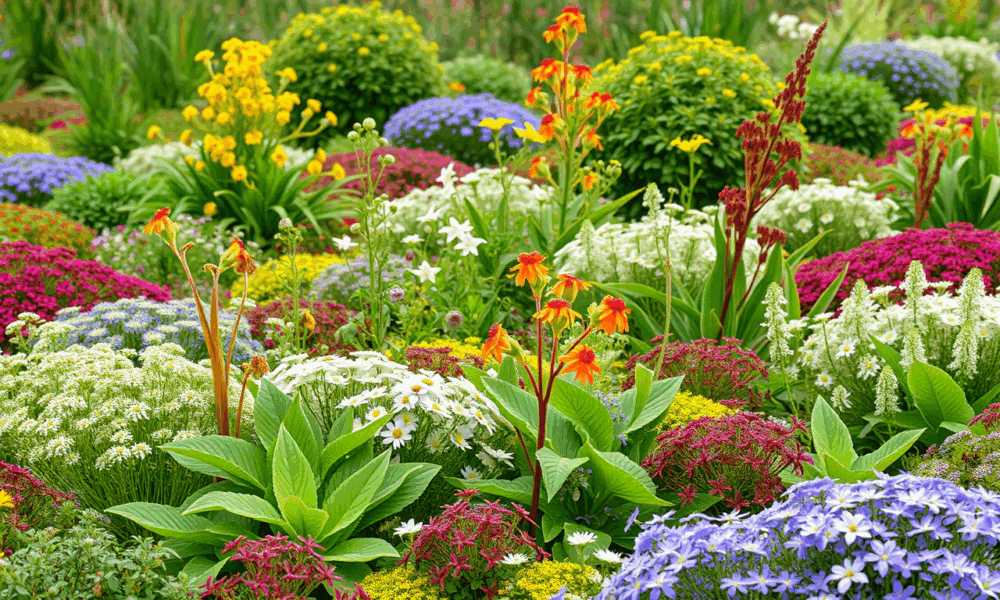



A new study shows that an unassuming plant has some very unusual family dynamics.



More than a decade ago, researchers launched the BabySeq Project, a pilot program to return newborn genomic sequencing results to parents and measure the effects on...
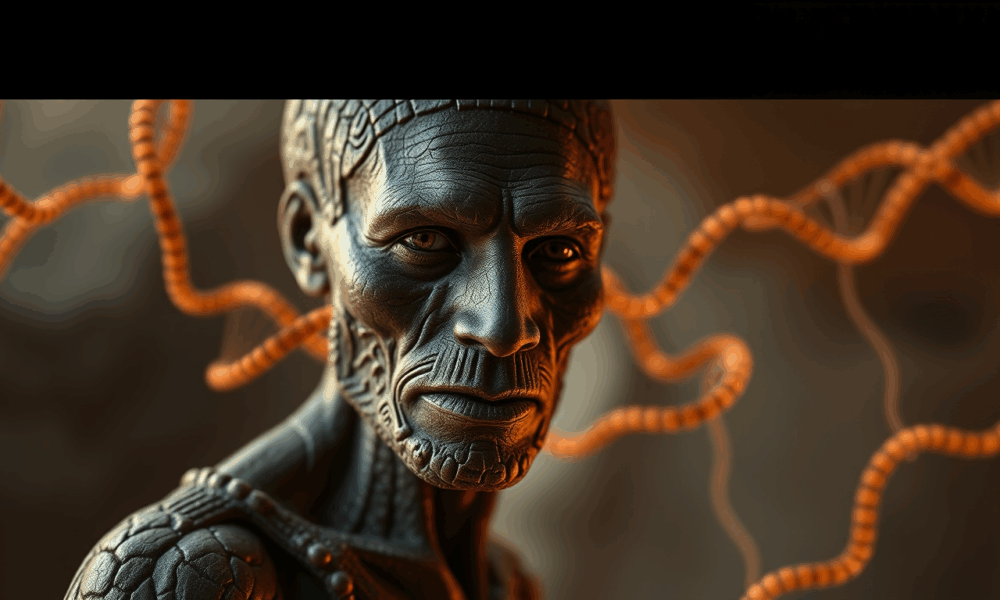



Modern HIV medicine is based on a common genetic mutation. Now, researchers have traced where and when the mutation arose -- and how it protected our...
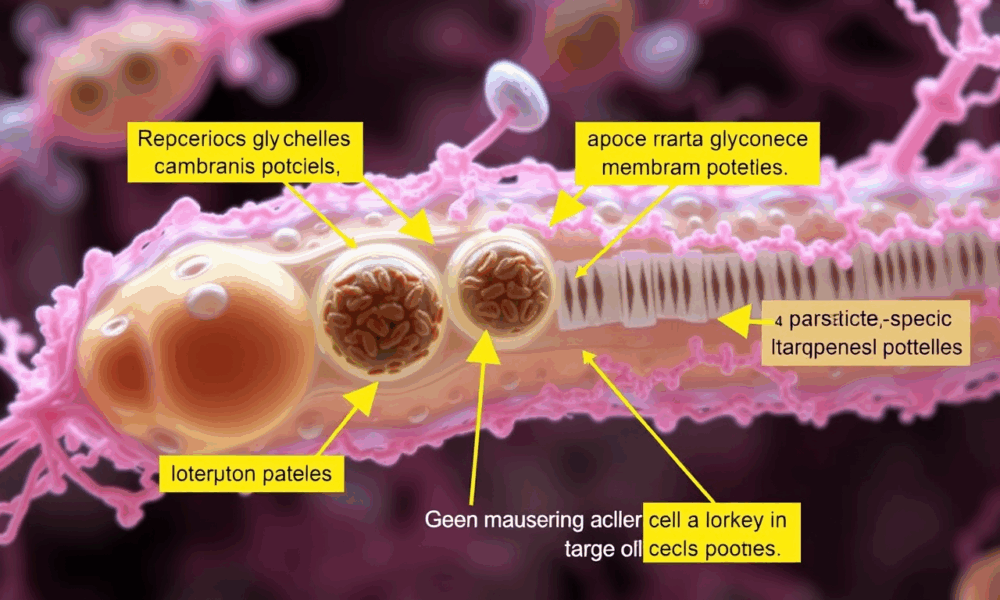
The efforts of a research team give hope for new treatment approaches for dangerous tropical diseases. The researchers have compiled a high-precision inventory of the membrane...
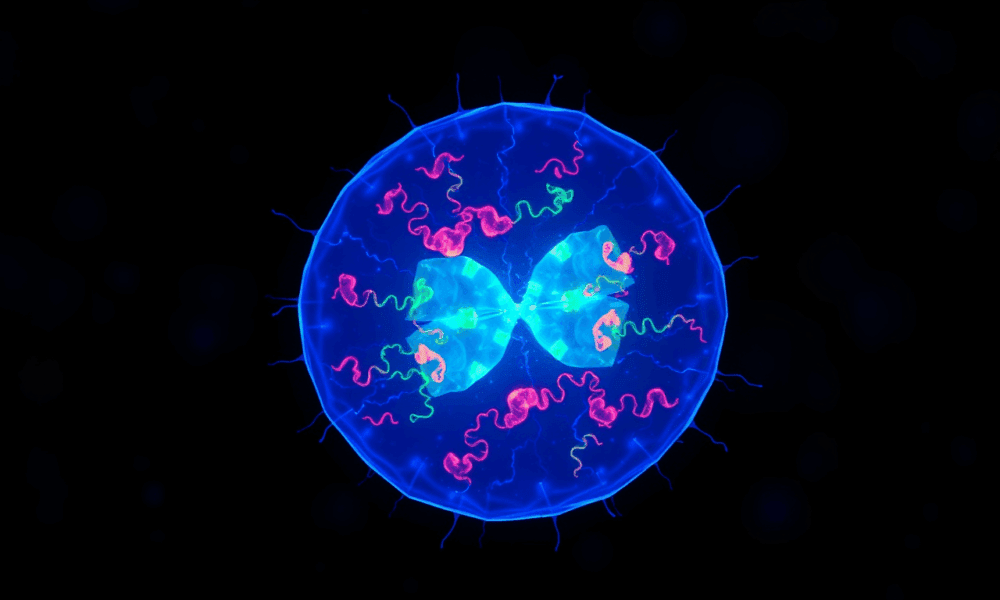
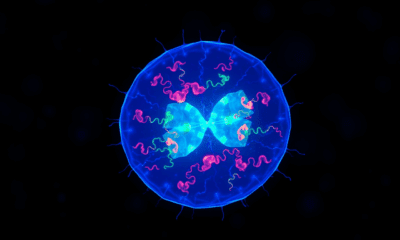
The Min protein system prevents abnormal cell division in bacteria, but is poorly understood. Researchers have uncovered how engineered e.coli bacteria control protein levels for maximum...
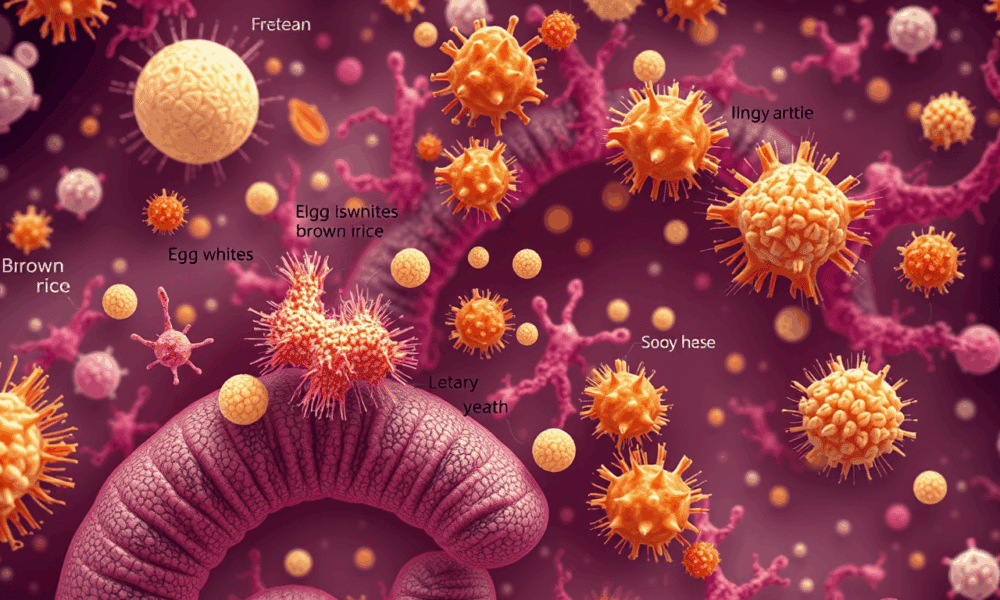
Protein sources appear to have major effects on both the population and function of the mouse gut microbiome.
An international team has identified a potential microbial culprit behind the alarming rise in early-onset colorectal cancer: a bacterial toxin called colibactin. Scientists report that exposure...
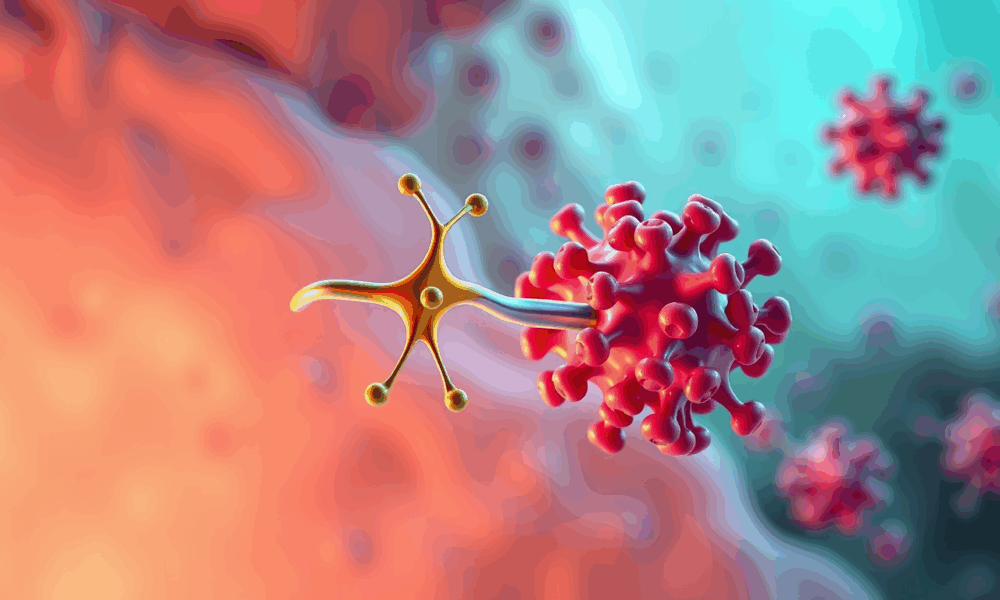
Scientists have discovered how chemokines and G protein-coupled receptors selectively bind each other to control how cells move.