While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Biology
Yeast Revolutionizes Human Protein Production with DNase1 Breakthrough
The protein DNase1 is one of the oldest biological agents in history: It has been on the market since 1958 and is now used, among other things, to treat cystic fibrosis. However, it takes considerable effort to produce it in immortalized hamster cells. This process is also costly. It would be far more cost-effective to produce it with undemanding yeast cells.

Behavioral Science
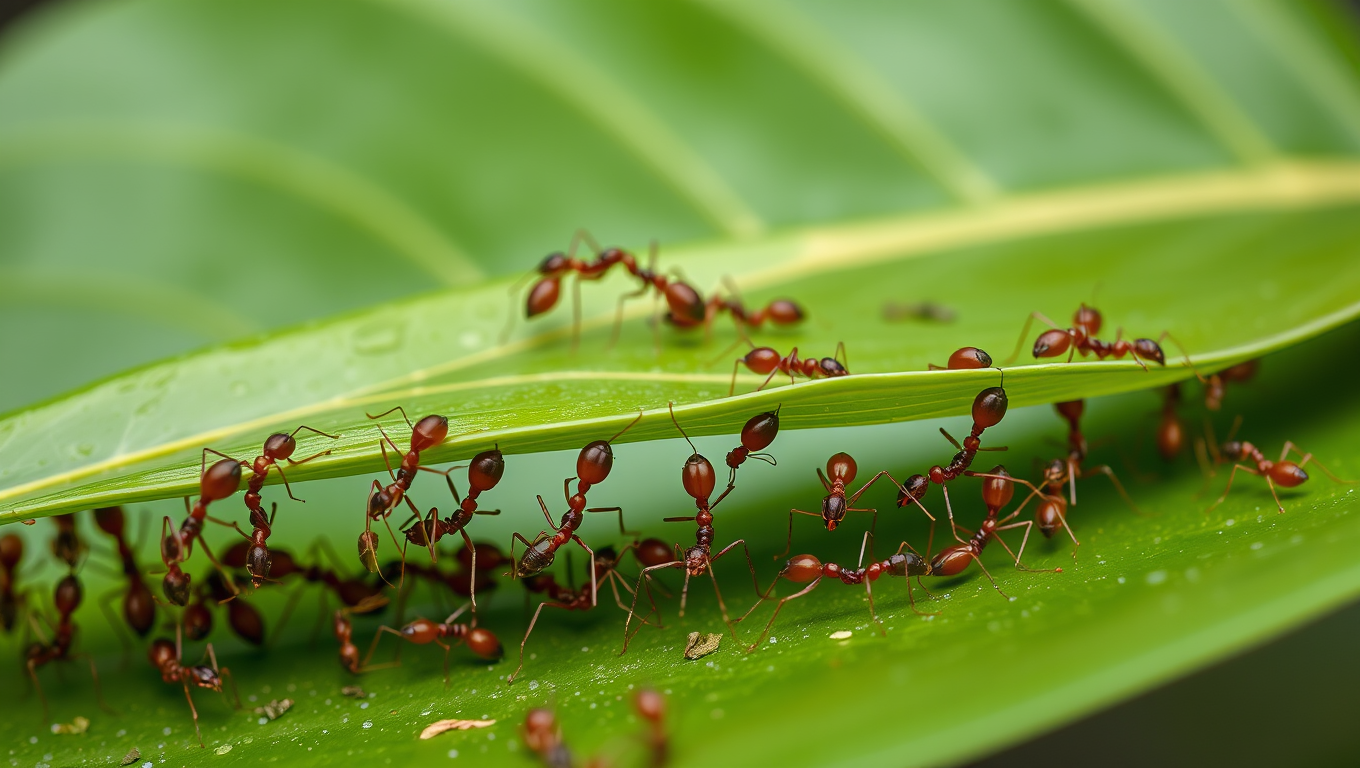
The Amazing Ant Strategy That Can Revolutionize Robotics
Weaver ants have cracked a teamwork puzzle that humans have struggled with for over a century — instead of slacking off as their group grows, they work harder. These tiny architects not only build elaborate leaf nests but also double their pulling power when more ants join in. Using a “force ratchet” system where some pull while others anchor, they outperform the efficiency of human teams and could inspire revolutionary advances in robotics cooperation.
Bacteria
Unlocking the Secrets of Mars: Cosmic Rays Reveal Hidden Potential for Life
Cosmic rays from deep space might be the secret energy source that allows life to exist underground on Mars and icy moons like Enceladus and Europa. New research reveals that when these rays interact with water or ice below the surface, they release energy-carrying electrons that could feed microscopic life, a process known as radiolysis. This breakthrough suggests that life doesn’t need sunlight or heat, just some buried water and radiation.
Animals
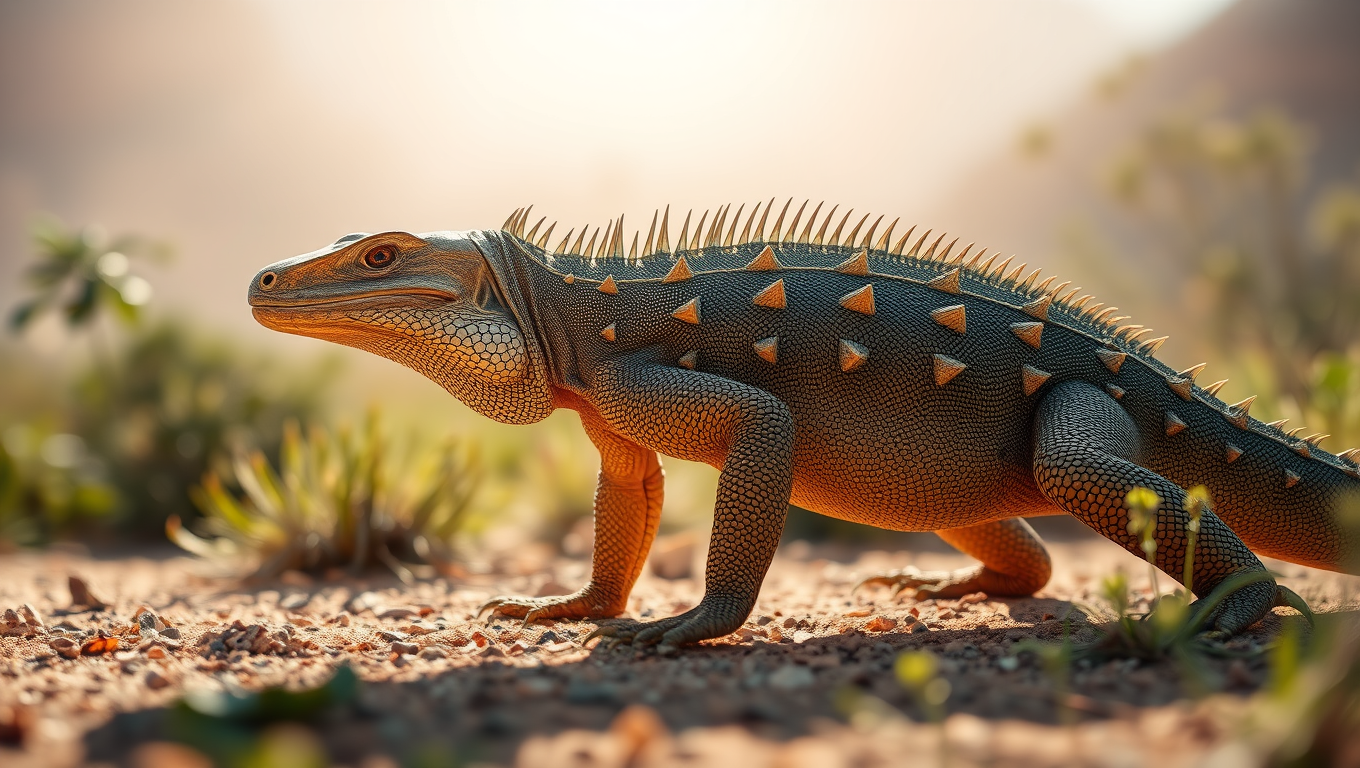
The Hidden Armor of Australia’s Iconic Lizards: Uncovering the Secret Bone Structures that Helped Them Thrive
Scientists have uncovered hidden bony armor—called osteoderms—beneath the skin of 29 goanna species across Australasia, a discovery that radically changes what we thought we knew about lizard evolution. Using museum specimens and advanced scanning, researchers found these structures are far more widespread than previously known, suggesting they may help with survival in harsh environments, not just offer protection. The revelation redefines how we understand lizard adaptation, ancient evolution, and the untapped potential of museum collections.
-

 Detectors11 months ago
Detectors11 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate12 months ago
Earth & Climate12 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer12 months ago
Cancer12 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein12 months ago
Albert Einstein12 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry11 months ago
Chemistry11 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Agriculture and Food12 months ago
Agriculture and Food12 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions12 months ago
Diseases and Conditions12 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention