While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Anthropology
“The Ancient Land Bridge: How Mantle Activity United Asia and Africa, Shaping Animal Evolution and Climate Patterns”
What roils beneath the Earth’s surface may feel a world away, but the activity can help forge land masses that dictate ocean circulation, climate patterns, and even animal activity and evolution. In fact, scientists believe that a plume of hot rocks that burst from the Earth’s mantle millions of years ago could be an important part in the story of human evolution.

Animals
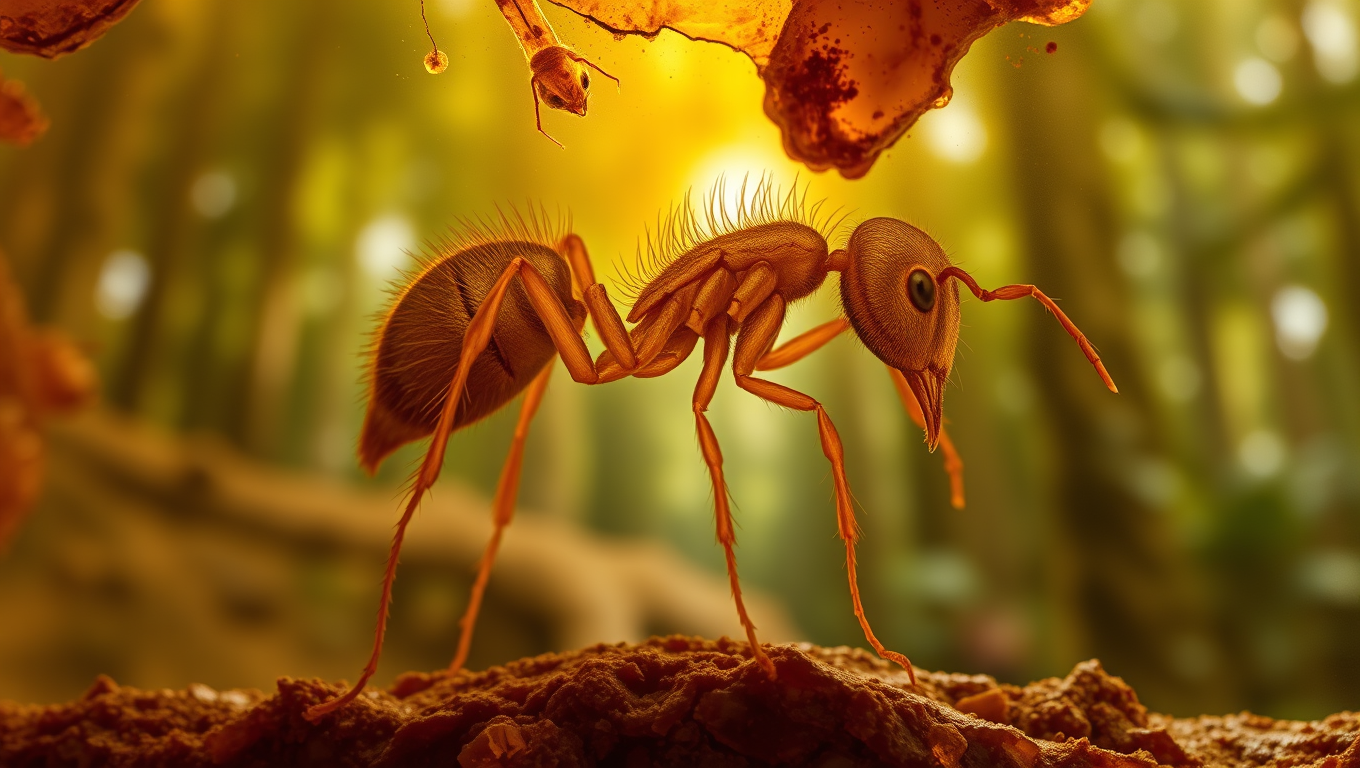
Unveiling the Ancient Secrets of the Dirt Ant: A 16-million-year-old Fossil Reveals the Smallest Predator Ant Ever Found
A fossilized Caribbean dirt ant, Basiceros enana, preserved in Dominican amber, reveals the species ancient range and overturns assumptions about its size evolution. Advanced imaging shows it already had the camouflage adaptations of modern relatives, offering new insights into extinction and survival strategies.
Ancient Civilizations
Unraveling a 130-Year-Old Literary Mystery: The Song of Wade Finally Solved
After baffling scholars for over a century, Cambridge researchers have reinterpreted the long-lost Song of Wade, revealing it to be a chivalric romance rather than a monster-filled myth. The twist came when “elves” in a medieval sermon were correctly identified as “wolves,” dramatically altering the legend’s tone and context.
Ancient Civilizations
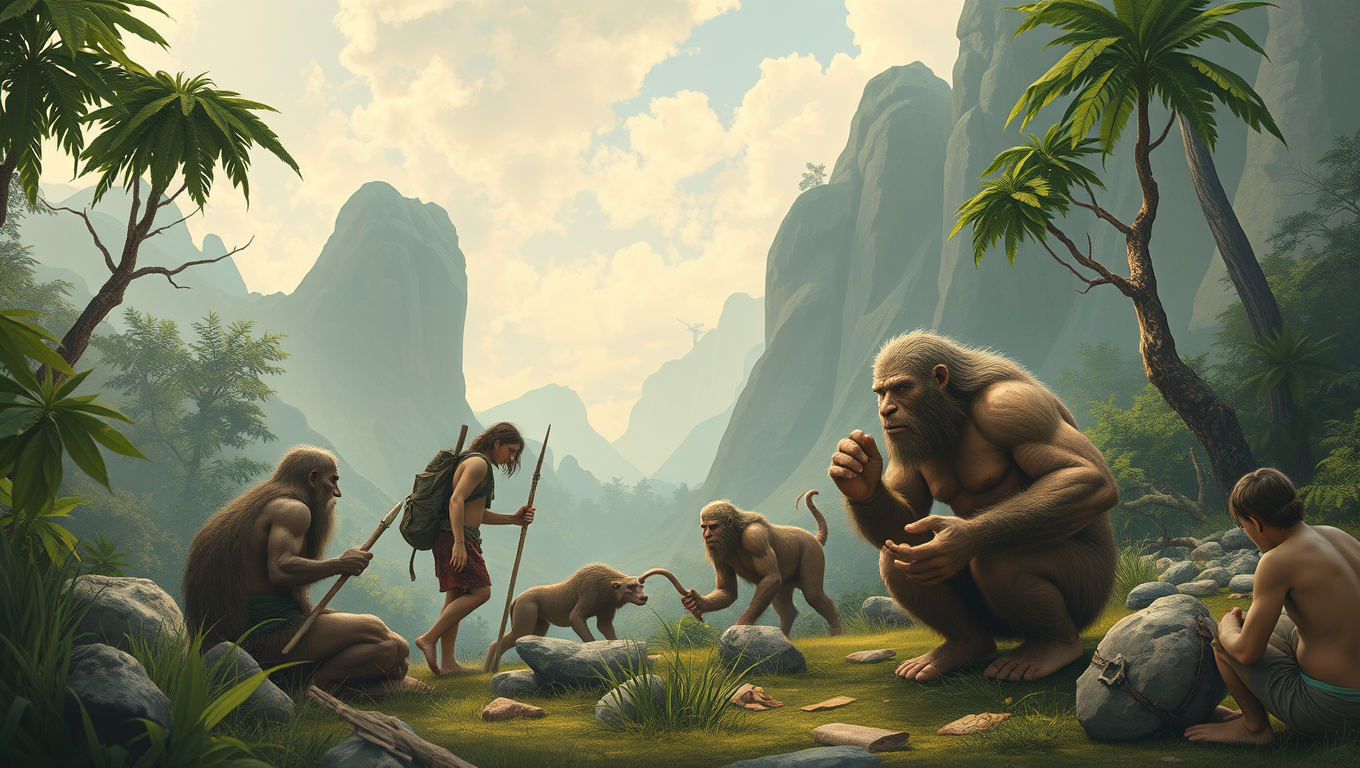
Uncovering Ancient Histories: Princeton Study Reveals 200,000 Years of Human-Neanderthal Interbreeding
For centuries, we’ve imagined Neanderthals as distant cousins — a separate species that vanished long ago. But thanks to AI-powered genetic research, scientists have revealed a far more entangled history. Modern humans and Neanderthals didn’t just cross paths; they repeatedly interbred, shared genes, and even merged populations over nearly 250,000 years. These revelations suggest that Neanderthals never truly disappeared — they were absorbed. Their legacy lives on in our DNA, reshaping our understanding of what it means to be human.
-

 Detectors10 months ago
Detectors10 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate11 months ago
Earth & Climate11 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer10 months ago
Cancer10 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Albert Einstein11 months ago
Albert Einstein11 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry10 months ago
Chemistry10 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate10 months ago
Earth & Climate10 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals
-

 Agriculture and Food10 months ago
Agriculture and Food10 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions11 months ago
Diseases and Conditions11 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention