While we try to keep things accurate, this content is part of an ongoing experiment and may not always be reliable.
Please double-check important details — we’re not responsible for how the information is used.
Biochemistry
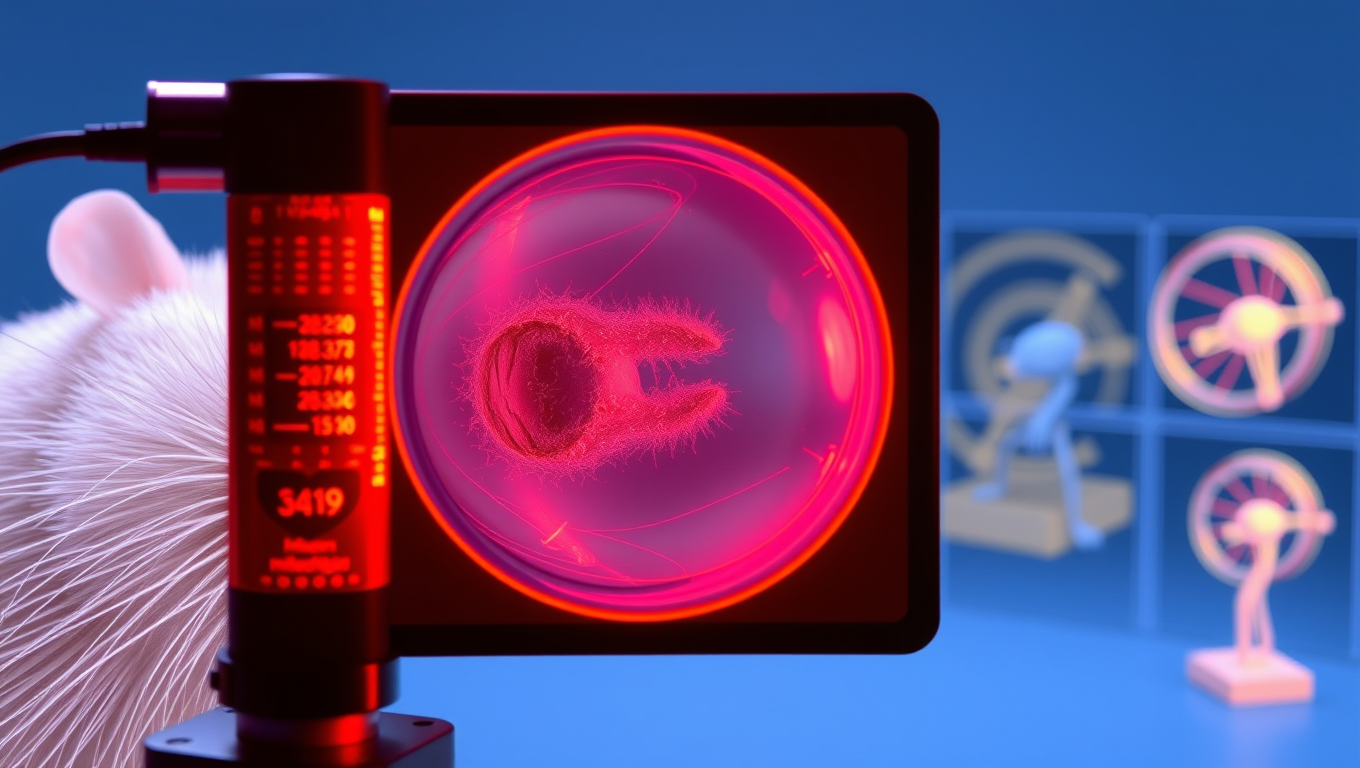
Breaking Ground: Terahertz Imaging Revolutionizes Cochlear Visualization
Researchers have discovered a groundbreaking use of terahertz (THz) imaging to visualize cochlear structures in mice, offering non-invasive, high-resolution diagnostics. By creating 3D reconstructions, this technology opens new possibilities for diagnosing hearing loss and other conditions. THz imaging could lead to miniaturized devices, like THz endoscopes and otoscopes, revolutionizing diagnostics for hearing loss, cancer, and more. With the potential to enhance diagnostic speed, accuracy, and patient outcomes, THz imaging could transform medical practices.

Biochemistry
Unveiling Molecular Motion: A Breakthrough in Synthetic Biology and Soft Matter Physics
Scientists have uncovered a previously unknown type of molecular motion inside DNA-based droplets: instead of spreading randomly, guest molecules advance in an organized wave. This surprising discovery opens the door to understanding how cells might organize internal processes without membranes. Using customizable DNA condensates as experimental models, the team showed how molecular waves emerge through precise DNA interactions. These insights could not only transform our grasp of cellular signaling but may even lay groundwork for treating neurodegenerative diseases by influencing how molecules behave inside aging cells.
Biochemistry
A Game-Changing mRNA Vaccine that’s More Effective and Less Costly to Develop
A new type of mRNA vaccine is more scalable and adaptable to continuously evolving viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 and H5N1, according to a new study.
Aerospace
Unveiling the Molecular Link Between Air Pollution and Pregnancy Risks: A Groundbreaking Study
A new study found exposure to specific tiny particles in air pollution during pregnancy are associated with increased risk of various negative birth outcomes.
-

 Detectors3 months ago
Detectors3 months agoA New Horizon for Vision: How Gold Nanoparticles May Restore People’s Sight
-

 Earth & Climate4 months ago
Earth & Climate4 months agoRetiring Abroad Can Be Lonely Business
-

 Cancer4 months ago
Cancer4 months agoRevolutionizing Quantum Communication: Direct Connections Between Multiple Processors
-

 Agriculture and Food4 months ago
Agriculture and Food4 months ago“A Sustainable Solution: Researchers Create Hybrid Cheese with 25% Pea Protein”
-

 Diseases and Conditions4 months ago
Diseases and Conditions4 months agoReducing Falls Among Elderly Women with Polypharmacy through Exercise Intervention
-

 Albert Einstein4 months ago
Albert Einstein4 months agoHarnessing Water Waves: A Breakthrough in Controlling Floating Objects
-

 Chemistry3 months ago
Chemistry3 months ago“Unveiling Hidden Patterns: A New Twist on Interference Phenomena”
-

 Earth & Climate3 months ago
Earth & Climate3 months agoHousehold Electricity Three Times More Expensive Than Upcoming ‘Eco-Friendly’ Aviation E-Fuels, Study Reveals